Did you know that you’ll have to pay a fine of up to Rs.1,00,000/- for non-filing of Form 24Q?
That sure got your attention, didn’t it?
But before we look at the penalties, let’s have a look at what Form 24Q is and how you can avoid these hefty penalties in the first place!
- What is Form 24Q?
- Who is responsible for filing Form 24Q?
- Requirements for filing Form 24Q
- Form 24Q consists of 2 Annexures
- Due dates for filing Form 24Q for FY 2022-23
- Submission of Form 24Q
- How to file Form 24Q through Asanify
- Penalties for not submitting Form 24Q
- Summary
- FAQs
What is Form 24Q – TDS return on Salary payment?
But wait, before we look into Form 24Q, what is TDS in the first place? So, who is responsible for TDS and why is it important? Let’s have a look!
What is TDS?
TDS stands for Tax Deducted at Source. It is deducted by the employer (the person who pays the salary to the employee).
TDS is a system in which tax is deducted at the source of income. Meaning? A person who is liable to pay tax (deductor or the employer) of any kind to any other person (deductee or the employee in this case), deducts tax at source and pays it to the Government.
Also, the deduction is done based on the employee’s monthly income and can vary between 1% to 10%
Why is the importance of Form 24Q?
Form 24Q is a form that has to be filled out and submitted on a quarterly basis. Why?
While paying salaries to employees, employers are required to deduct a certain amount of tax (Tax Deducted at Source, also known as TDS) under section 192. This form basically has to file the TDS return by filing out Form 24Q. You must mention information about the employer, employee, challan, employee’s salary as well as the TDS on salary in this form.
Another important thing to keep in mind is that at the end of the financial year, the employee can claim a certain amount which had been deducted. This information must be declared in Annexure II (which we will talk about later in this blog!)
Who is responsible for filing Form 24Q?
As seen previously, it is the employer’s responsibility. So, they are responsible for filing salary TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) in file Form 24Q if they exceed the basic exemption limit. The employer must file this form on a quarterly basis. Failure or even delay in doing so will result in heavy penalties.
If you are an employer and are in search of Form 24Q, you can either…
- Get it from the Income tax department website (e-filing), or,
- Download the soft copy by clicking here – Form 24Q download
Requirements for filing Form 24Q
While you may know what Form 24Q is, you also need a list of documents and details before you start filling out the form. I have listed them below.
Challan details
- Date of deposition of challan
- Challan serial number
- BSR code of branch
- Total Amount in Challan
- TDS amount allocated among deductees (employees)
- Interest amount allocated among deductees (employees)
Deductee or Employee details
- Name of the employee
- Employee reference number (if available)
- PAN of the employee
- Education Cess
- Deductee Type (Regular, Senior Citizen, Super Senior Citizen or Woman).
- Employment period.
- Gross Salary for the respective financial year.
- House rent paid, Home loan, any other investments u/s 80C,80D etc.
- TDS Section Code
- Date of payment/ credit
- Amount paid or credited
- TDS amount
- Any other income which the employee has disclosed.
Deductor or Employer details
- PAN
- TAN (TDS account number)
Also, if an employer does not deduct TDS, or deducts a lower amount than the requirement, he/she must provide the reason for doing so as well!
Difference between Annexure I and Annexure 2
There is majorly one difference between the 2. You need to submit Annexure I at the end of each quarter in the financial year. On the other hand, you (the employer) need to submit Annexure II only at the end of quarter 4, meaning, at the end of the financial year.
Let’s have a look at Annexures I and II
Annexure I of Form 24Q
In Annexure I, you, an employer have to fill in your own details along with that of challan and your employee’s. You will need to add information about each deductee i.e. employee alongside each respective challan.
In some situations, the employer does not deduct TDS or deducts a lower rate than what is mandated. In such a scenario, they are required to also mention the reason for lack of deduction (or less deduction) here in Annexure I.
You also need to remember to submit Annexure I at the end of every quarter (Q1, Q2, Q3, & Q4) of the financial year.
Annexure II of Form 24Q
This is different from Anexxure I primarily because you do not have to submit Annexure II at the end of every quarter. Instead, you must only file Annexure II at the end of the 4th quarter (Q4), meaning at the end of the financial year (FY).
This section also contains the salary details of the employee. Information such as salary break up, deductions to be claimed by the employee i.e. deductee, other sources of income, assets and tax liability.
Upcoming due dates for filing Form 24Q for FY 2022-23
It has 2 Annexures as we saw above. And each of them has different rules for submission. Let’s have a look at the due dates for the submission of Anexxure I and II respectively.
| Annexure | Quarter | Due dates |
| Annexures I & II | FY 2021-22 Q4 | 31st May 2022 |
| Annexures I | FY 2022-23 Q1 | 31st July 2022 |
| Annexures I | FY 2022-23 Q2 | 31st October 2022 |
| Annexures I | FY 2022-23 Q3 | 31st January 2023 |
| Annexures I & II | FY 2022-23 Q4 | 31st May 2023 |
Submission of Form 24Q
24Q can be submitted in 2 ways.
- Online
- Offline
However, in some cases, filing the document online is mandatory. In case you come under any of the following categories, then you are mandated to fill it out online!
- If the employer is a part of a government institution
- In case the employer is the principal officer of a company
- If you, the employer have had your accounts audited for the last year (under the Income Tax Act, Section 44AB)
- In case the records of the number of employees or deductees in a report at any period in the financial year are greater than 20
How to file Form 24Q through Asanify
Time needed: 5 minutes.
You can easily generate and file form 24Q via Asanify by following these simple steps
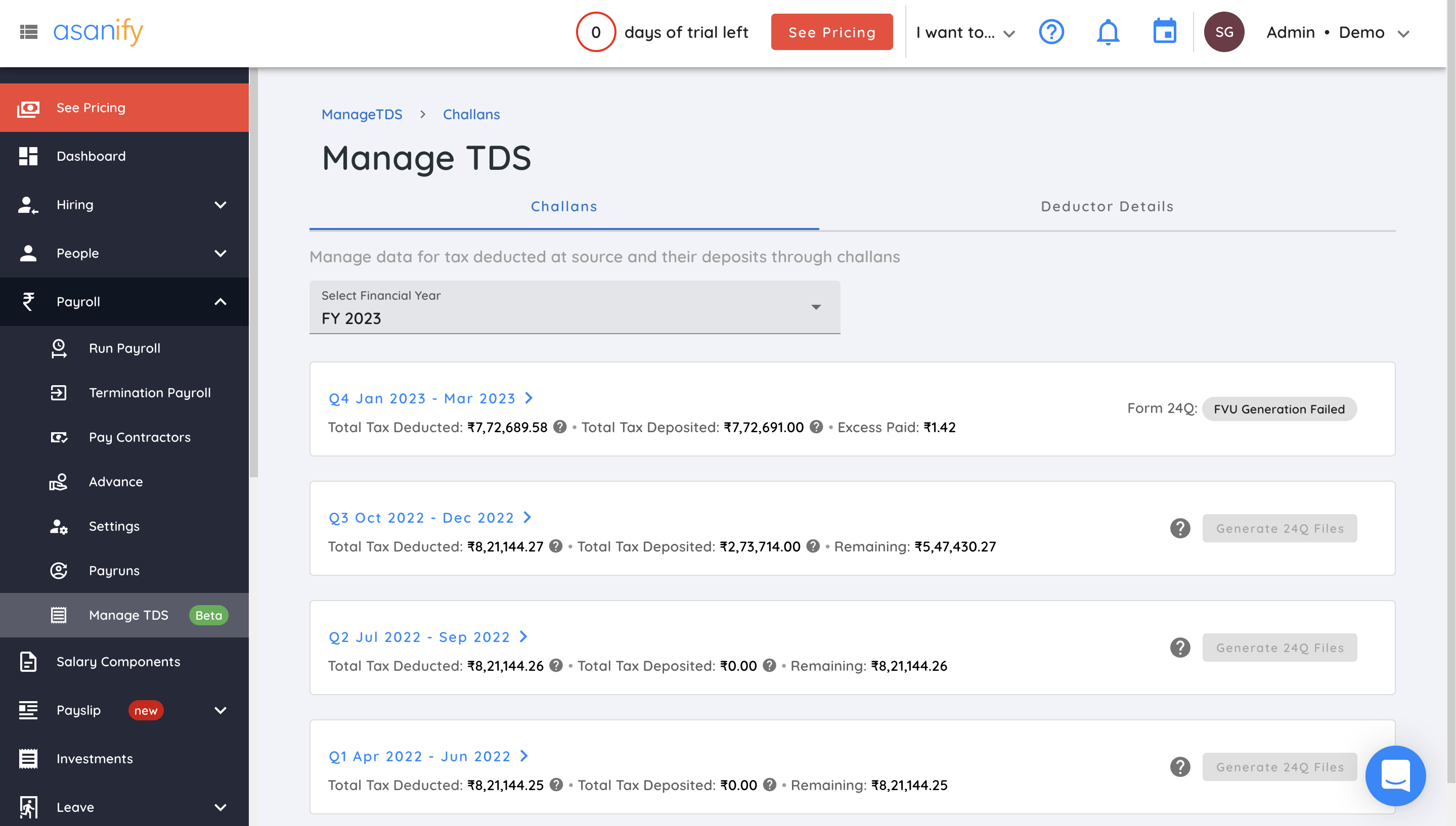
- Go to the ‘Manage TDS’ section on the left navigation bar
The ‘Manage TDS’ button is under the payroll section in the left navigation bar. Here, you will see two major sections – Challans and deductor details. Once you’re in the ‘Challans’ section, you will get a drop-down where you will be able to select the financial year.

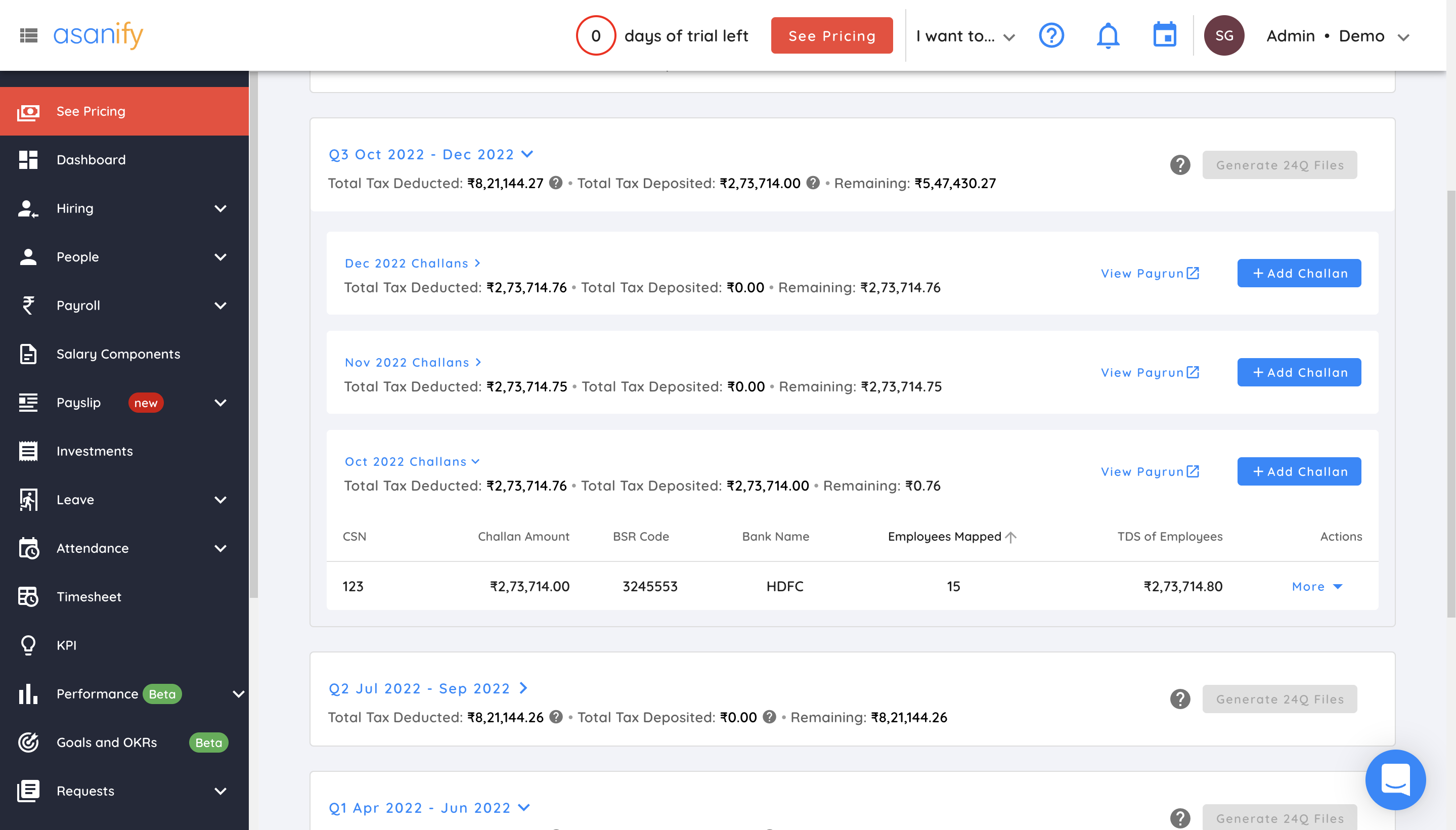
- Select the financial year and go to the quarter for which you wish to generate form 24Q
As you can see below, the button on the top right to generate 24Q files option is disabled. It will get enabled once you have added the challan details for each month of the quarter

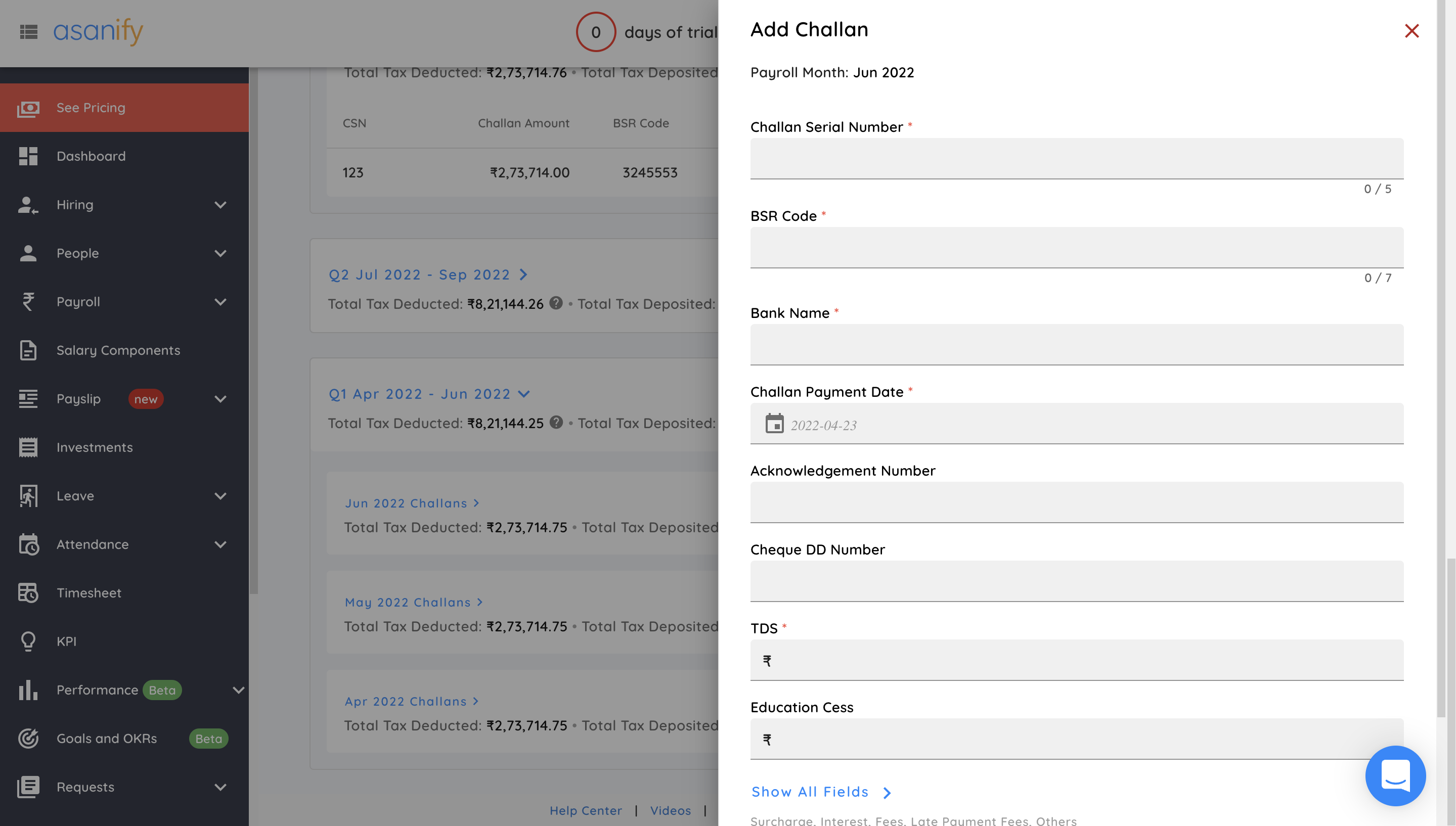
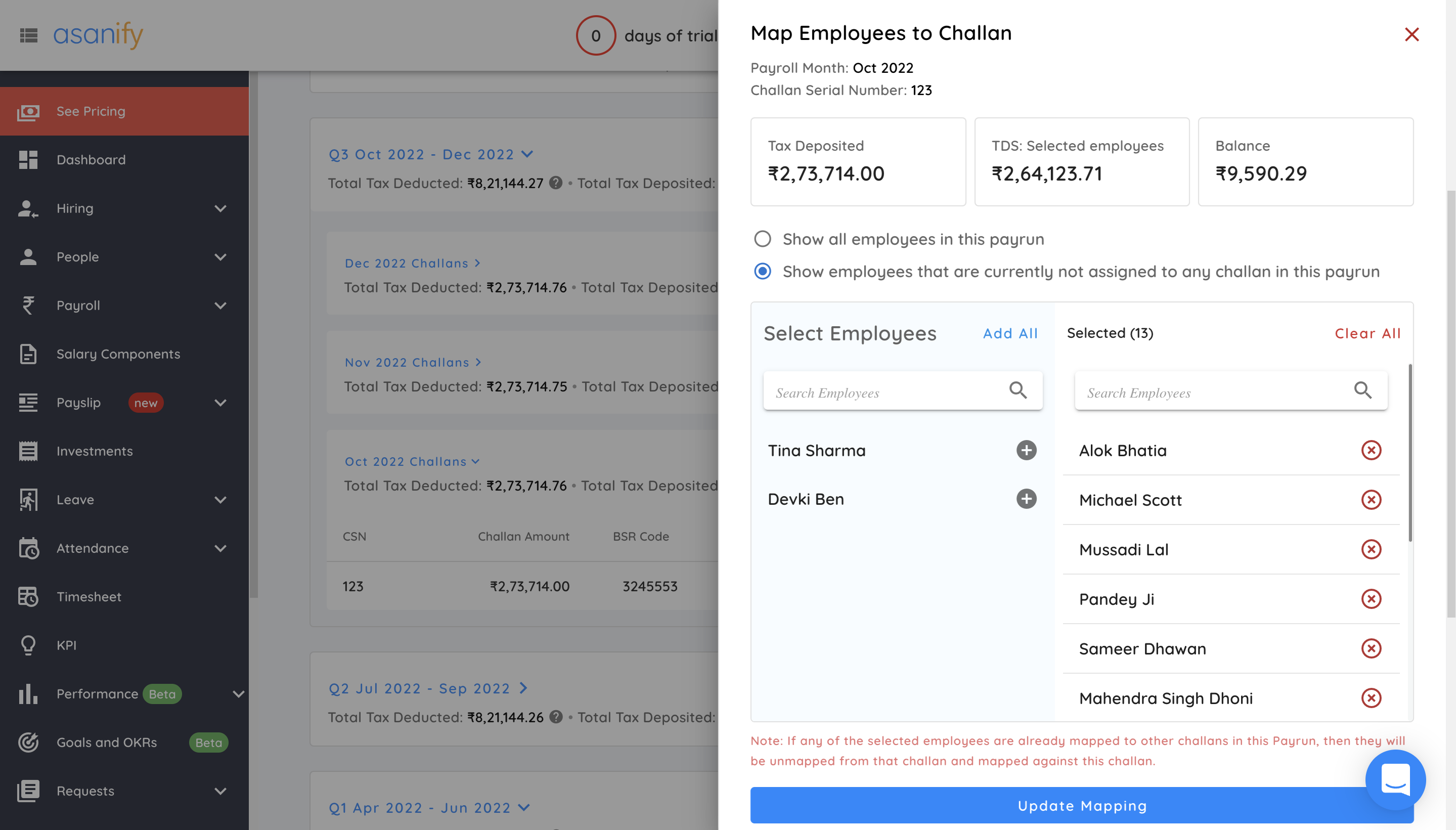
- Map challan details for each employee
Once you have added the Challan details for each employee, go ahead and follow steps 2 and 3 for each of the other months of the same quarter.

- After you have added all the challan details, click on ‘Update Mapping’

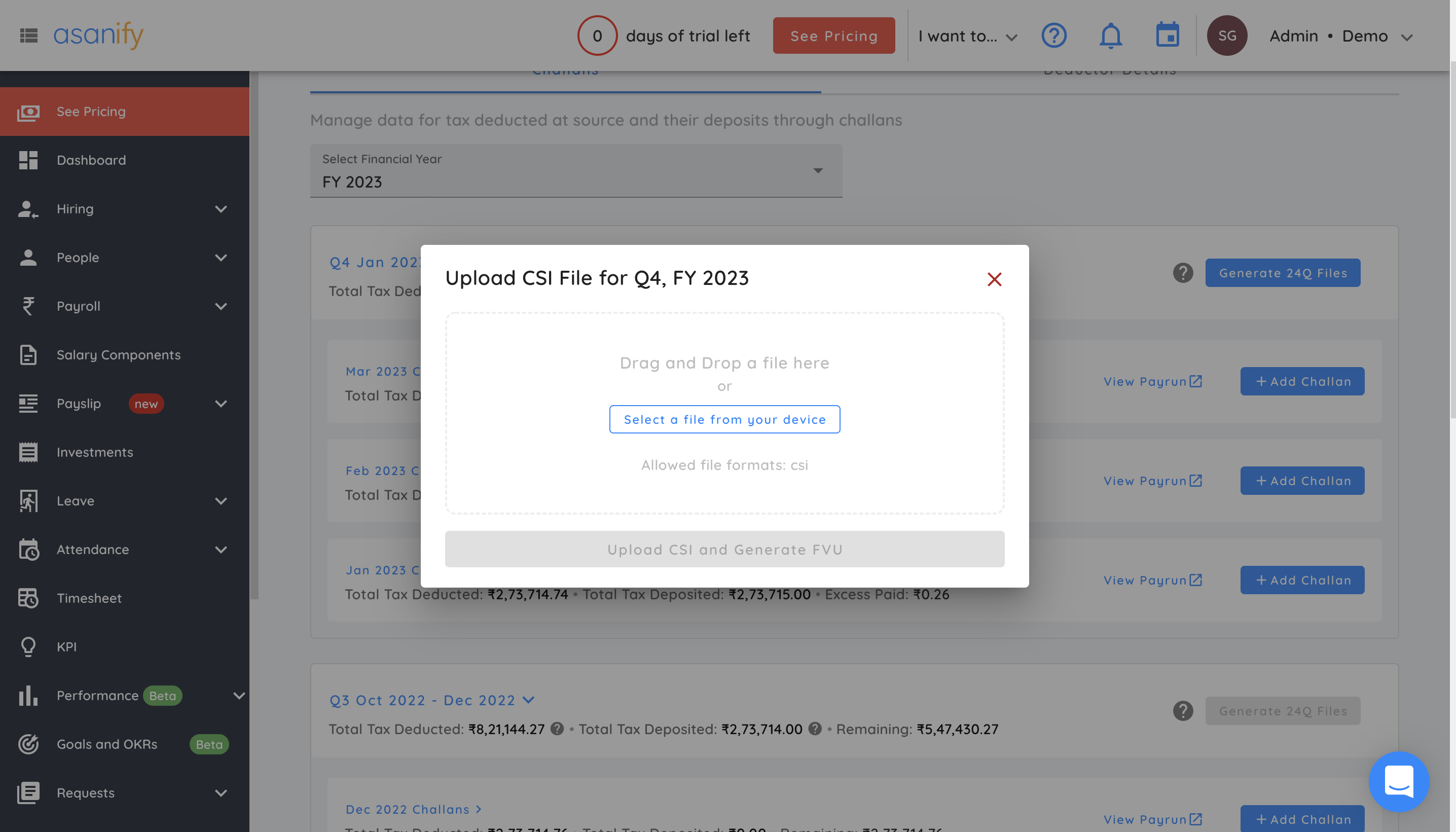
- Upload a CSI file with all the Challan details for that quarter
The ‘generate 24Q files’ button that was initially disabled will now be enabled for you to generate the form. Click on it to upload the CSI file.

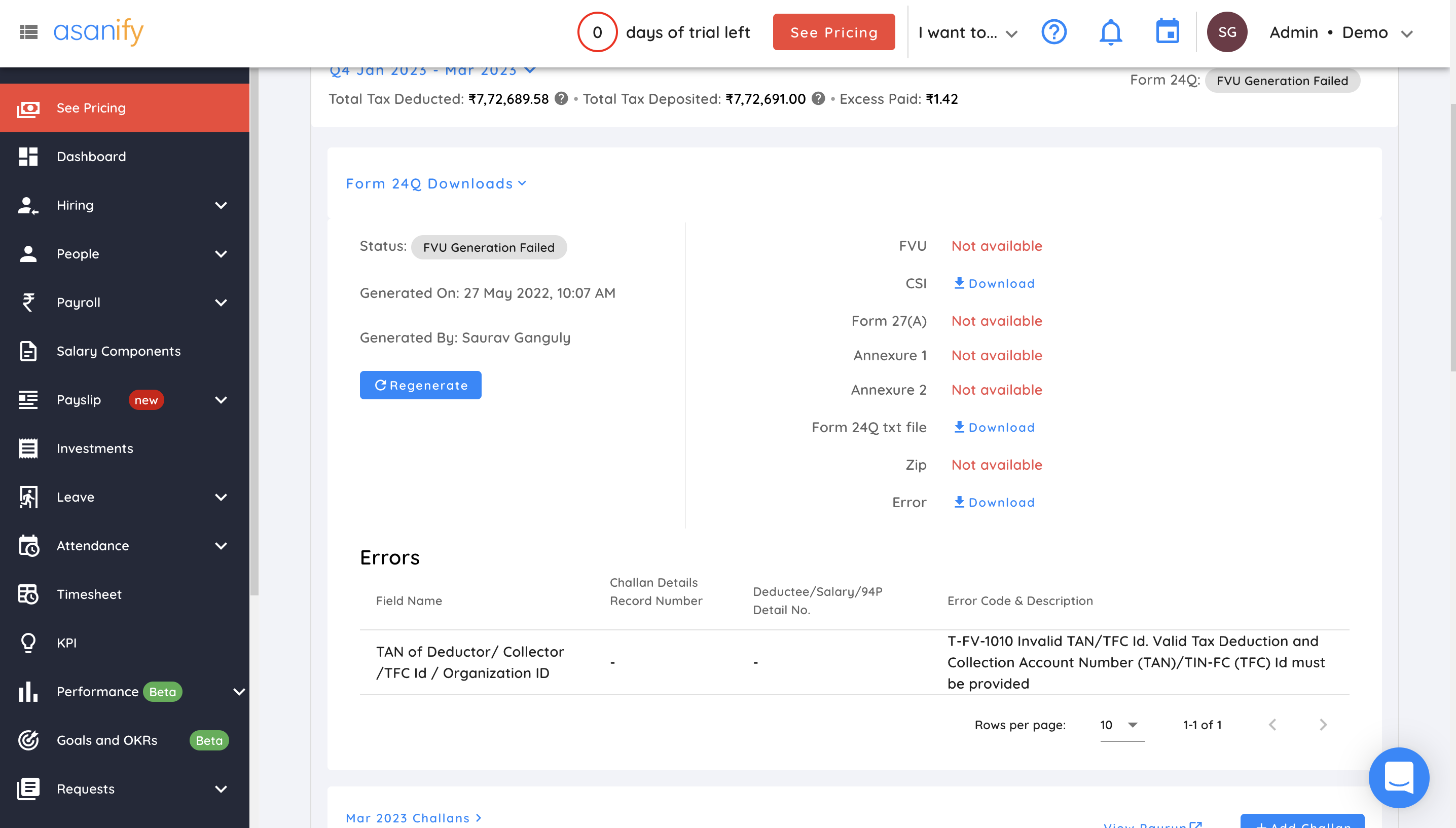
- Correct errors in the data (if any)
If there are any errors in the data uploaded, the system will show you exactly where they are. You can correct these errors and click on the ‘Re-generate’ button. Form 24Q will be generated!!

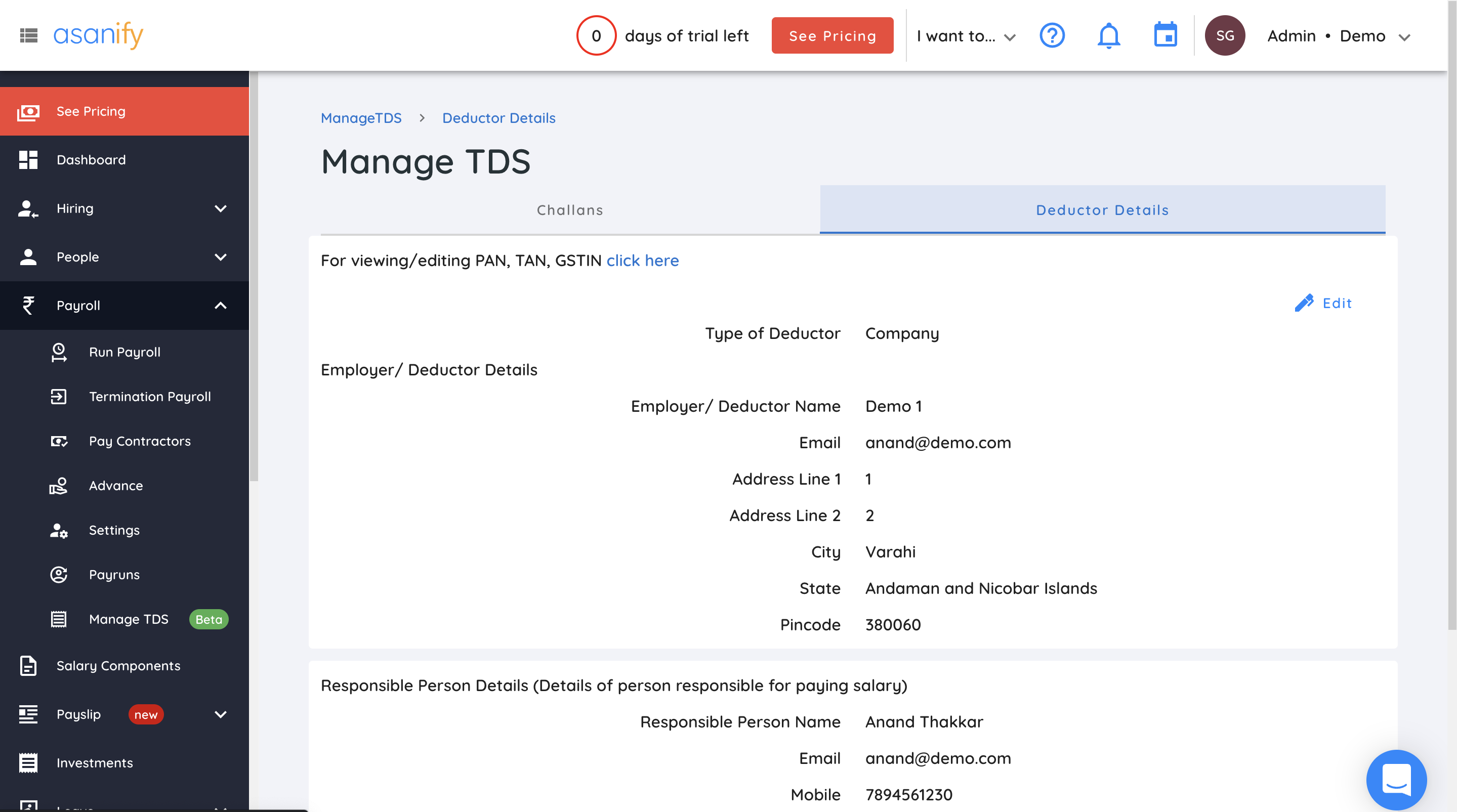
- You can also keep track of the deductor (employer’s) details in the ‘Manage TDS’ section as shown below

Penalties for not submitting Form 24Q
The employer is exempted from the penalty – under 271H if and only if-
- TDS is deposited to the government
- Late filing fees and interest (if any) are also deposited
- Return is filed before the expiry of 1 year from the due date
However, you could be charged an extremely hefty fee if you haven’t filed Form24Q accurately and on time! Rather than reading on to find out what the fines are, I suggest you submit the form on time instead.
In any case, if you have found yourself in a situation where you need to know the penalties, they are mentioned here below.
- For late deduction, 1% per month, starting from the due date up until the actual date o deduction
- In the case of late deposit of TDS, 1.5% per month, starting from the due date up until the actual date o deduction
- For Late Filing Fees– under section 234E, the employer must pay a fine of Rs. 200 per day is to be paid until the return is filed. The employer must pay this amount for each day until the total fine becomes equal to the TDS amount.
- The penalty under 271H – In addition to fees to be paid under 234E, the employer may be charged a penalty of a minimum of Rs. 10,000 and maximum Rs. 1,00,000.
Summary
Now you know exactly what Form 24Q is and how to fill it! So, remember,
- You must submit Annexure I at the end of every quarter
- Annexure II has to be submitted only after Q4 (quarter 4) meaning at the end of the financial year
- There is a list of documents and details you need to keep handy while filling out this form. Click here to revisit that section
- Not deducting or depositing TDS can result in you having to pay some serious penalties. File Form 24Q on time!
FAQs
The employer is responsible for filing Form 24Q. He is expected to submit Annexure I at the end of every quarter and Annexure II only at the end of quarter 4, meaning at the end of the financial year!
While paying salaries to employees, employers are required to deduct a certain amount of tax under section 192. This form basically has to file the TDS return by filing out Form 24Q. You must mention information about the employer, employee, challan, employee’s salary as well as the TDS on salary in this form.
Yes, for all those who fall under the tax slab prescribed by the income tax department, filing Form 24Q is mandatory.
The employer or the organization is responsible for deducting TDS and filing Form 24Q
Not to be considered as tax, legal, financial or HR advice. Regulations change over time so please consult a lawyer, accountant or Labour Law expert for specific guidance.