Employees’ State Insurance is an essential payroll compliance in India. In this blog today, I will cover necessary details about ESI. If you are running a startup or a small business, read on. The essential target by the Government of India to dispatch the Employees’ State Insurance (ESI) scheme is to cover workers from health and wellness issues.
Such issues include:
- lasting or impermanent disablement,
- disorder,
- demise because of employment injury or occupational disease,
The ESI scheme empowers workers to avoid monetary loss due to such tragic situations. Additionally, the scheme likewise offers maternity benefits to the beneficiaries.
In this article, I will be talking about everything you need to know about the Employees’ State Insurance Scheme.
- What is ESI – Employees’ State Insurance scheme?
- What is the applicability and extent of coverage of ESI?
- Which are the entities covered under ESI?
- Which documents are required for ESI registration?
- What is the Eligibility for ESI?
- Procedure For ESI Registration
- How does a new employee become a member of the Scheme?
- What are the ESI contribution rates?
- How do you calculate ESI?
- What are the returns that are filed every year after the registration is finalized?
- How to file the Monthly Contribution and Payment of dues for ESI?
- What is the deadline for ESI?
- Which are the benefits under ESI?
- What to do to claim ESI benefit?
- How To Check Claim Status of ESI Online?
- How an Automated Payroll Software helps implement Rules for ESI and PF Deduction.
- What is the infrastructural network of ESI?
- What is the Role of ESIC in securing social security?
- Which prospects are Covered Under Employees’ State Insurance Scheme?
- Which prospects are Not Covered Under Employees’ State Insurance Scheme?
- What are the futures prospects of ESI?
- FAQ
What is ESI – Employees’ State Insurance scheme?
ESI scheme is a cover for workers which protects them with medical care for the insured. Additionally their dependents are covered as well. Finally ESI offers a variety of cash benefits during loss of wages or disablement. Also, the scheme offers pension known as dependent benefit to the family members of the insured person in case of death or injury due to occupational hazards while at work. Note that ESI is one of the key payroll compliances along with Provident Fund (PF), Professional Tax (PT) and TDS.
Employees State Insurance Act, 1948
The Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948 or popularly known as the ESI Act was notified by the Parliament and it was the first major legislation on the Social Security for workers post-independence of the country.
The ESI Act 1948 provides medical cover and other essential benefits to workers and employees who are working in factories, business establishments and organizations such as:
- hotels
- road transport
- cinemas
- newspaper
- educational or medical institutions
- shops
- wherein 10 or more persons are employed.
The ESI scheme offers benefits to both the workers and their dependents in case of any unfortunate eventualities at work. Under the ESI Act, employees or workers employed at the
- above-mentioned categories
- earning wages up to INR 21,000 per month
are entitled for this social security scheme. The ESI Act aims at respecting human dignity during crises by protecting them from destitution, deprivation and social degradation.
What is the applicability and extent of coverage of ESI?
- Stretches out to the entire of India and covers all business environments enlisted under either in the Factories Act or under the Shops and Establishments Act, where at least 10 employees are working.
- An employee is obligatorily needed to be covered by her/his employer as long as s/he is within the threshold reaches of wages.
- For example, all such workers whose monthly salary are up to and equivalent to Rs.21,000/month, it is the obligation of the business to get qualified representatives covered under the ESIC scheme.
- Monthly salary limit for inclusion under the ESIC scheme for representatives with incapacity is Rs.25000/month rather than Rs.21,000 in other cases.
Which are the entities covered under ESI?
- Shops
- Restaurants or Hotels only engaged in sales.
- Cinemas
- Road Motor Transport Establishments;
- Newspaper establishments (which is not covered under the factory act)
- Private Educational Institutions
Which documents are required for ESI registration?
The documents required for the registration are –
1. A registration certificate obtained either under the:
- Factories Act
- Shops and Establishment Act
2. Certificate of Registration in case of Company, and Partnership deed in case of a Partnership.
3. Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association of the Company.
4. A list of all the employees working in the Establishment.
5. PAN Card of the Business Entity as well as all the Employees working under the entity.
6. The compensation details of all the employees.
7. A cancelled cheque of the Bank Account of the Company.
8. List of Directors of the Company.
9. List of the Shareholders of the Company.
10. Register containing the attendance of the employees.
After collecting all the above-mentioned documents the following procedure is to be followed for the registration of the ESI:
- Form No – 1 (Employers Registration Form) is to be downloaded and filled.
- After downloading the PDF version of the form and filling it, it also has to be submitted on the ESIC website itself along with the above mentioned documents.
What is the Eligibility for ESI?
To be eligible for the ESI scheme, the employee or the worker’s monthly salary should not exceed Rs.21,000 and Rs.25,000 for people with disability.
-
For companies not registered under the ESI Act
Companies that have an employee base of more than 20 must be registered under the act.
-
For companies already registered under the ESI Act
The organizations need to rework the CTC of all the employees who have a monthly gross salary of INR 21,000 or less.
Procedure For ESI Registration:
The procedure for ESI registration by the employers is completely online and does not require submission of physical application either before or after the registration. Here are the steps to register your company with the ESIC:
- Visit the ESIC Portal and click on ‘Login’.
- On the new page, click on ‘Sign Up’.
- Enter your company name, employer name, state, region, email ID (which will be your username), and your phone number.
- Click on the checkbox to confirm your company or factory is under an exclusive labor contract, manpower suppliers, security agencies or contractors supplying labor categories.
- Click on ‘Submit’. An email will be sent with login credentials or details.
- Now that you have signed up, you need to visit the ESIC Portal to login.
- Enter the username and password received by email and click on ‘Login’.
For new employee registration
8. Click on ‘New Employer Registration’.
9. Select the type of unit and click on submit.
10. On the new page, enter the name of the unit, complete postal address of the factory or the establishment and the police station under whose jurisdiction your unit is.
11. Enter if the building or the premises of the factory or the establishment is owned or hired and click on ‘Next’ to proceed.
12. Enter the nature of the business and category, PAN details, etc. and click on ‘Next’.
13. On the next page, enter the date of commencement of the factory or establishment and license details (if any).
14. Now, select the constitution of ownership and details of owners and then click on ‘Save’ after entering all the designation of owners and then click on ‘Next’.
15. Here, enter the number of employees working in your establishment or factory and the number of employees earning less than Rs.21,000 and click on ‘Save’.
16. In the new page, enter the date when the first 10/20 employees were employed and then click on ‘Employee Declaration Form’.
17. Select ‘Yes’ if the insured person is already registered and enter IP number and date of joining. Select ‘No’ if IP is not registered and click on ‘Continue’.
To submit
18. Enter the name of the IP and also father’s name, address, date of birth, gender, marital status, family details and date of joining.
19. Now, click on the checkbox also and click on ‘Submit’.
20. Once all details are duly filled, click on ‘Close’ on the new page.
To download Challan for future reference:
21. On the new page, select the respective ESI branch office and the inspection division.
22. Now, also click on the checkbox to declare that information provided is correct and then click on ‘Submit’. You’ll be redirected to a new page.
23. On the new page, you will have to also click on ‘Pay Initial Contribution’ and click on ‘Submit’. You will be provided with a Challan Number for future reference.
24. Click on ‘Continue’ to pay through the required payment gateway.
Once the payment process is completed, you will receive the system generated ESI Registration Letter known as C-11 to your registered email ID. The C-11 acts as proof of registration of the company with the ESIC.
How does a new employee become a member of the Scheme?
In the event that monthly salary are up to and equivalent to Rs.21,000 at that point within 10 days of joining of another representative. It is the duty of the Employer to guarantee that such new worker and his family or wards are covered under the Scheme and a insurance number is apportioned to the employee.
When the employee is enrolled under the Scheme, various benefits are also currently accessible to the guaranteed worker for self and his relatives or wards.
Because of consistently expanding industrialization and an ever increasing number of individuals; relocating from towns and more modest towns to metropolitan regions have come about into partition of individuals from their relatives as in the majority of the cases the working environment of a worker is other than his local spot.
To also guarantee all qualified individuals get benefits as and when required now-a-days, ESIC issues:
- 2 protection card famously known as ‘Pehchaan Card” – 01 for the employee
- and other one which is linked with the insured employee for the family members so that both can enjoy benefits under the scheme at their respective place of living.
Greatest benefit of the Scheme is that no furthest constraint of clinical costs is Capped likewise in the event that,
if ESIC clinic doesn’t have:
- needed prescriptions
- gear, offices
- or authority specialists
then ESIC alludes such patient/employee or affected family member to private hospital having such facilities and reimburse the bills directly to the service provider hospital.
What are the ESI contribution rates?
Both the employer and the employee contribute to also collect the funds for the ESI scheme. Earlier this contribution was:
- 6.5% in total with
- 4.75% as the employer’s fund
- and remaining 1.75% as the employee’s part.
But now, as per the latest ESIC rule:
- the employee’s contribution is 0.75%
- and the employer’s share is 3.25%
- making it a total of 4% of the employee’s monthly wages.
Collection of ESI Contribution
It is the employers responsibility to contribute to the ESI fund by deducting the employees’ contribution from wages and combining it with their own contribution.
An employer is expected to deposit the combined contributions within 15 days of the last day of the Calendar month. The payments can also be made online or to authorized designated branches of the State Bank of India and some other banks.
What salary components are applicable to ESI deductions?
ESI contributions (from the employee and employer) are calculated on the employee’s gross monthly salary.
Most people face challenges in understanding ESI deduction rules because they aren’t clear about the concept of Gross Salary. So let us explain this concept first.
Gross salary is described as the total income earned by the employee, while working in their job, before any deductions are made for health insurance, social security and state and federal taxes.
For ESI calculation, the salary comprises of all the monthly payable amounts such as:
- Basic pay,
- Dearness allowance,
- City compensatory allowance,
- House Rent Allowance (HRA),
- Incentives (including sales commissions),
- Attendance and overtime payments,
- Meal allowance,
- Uniform allowance and
- Any other special allowances.
The gross monthly salary, however, does not include Annual bonus (such as Diwali bonus), Retrenchment compensation, and Encashment of leave and gratuity.
Also Read: Understanding the Salary Structure in India
How do you calculate ESI?
ESI calculation comprises of various elements of an employee’s monthly salary such as Basic Pay, Dearness Allowance, City Compensatory Allowance, HRA, Incentives, Attendance and Overtime Payments, Meal Allowance, Uniform Allowance and other special allowances.
- Let’s take an example and do the math to get a fair idea of the calculation.
- Let the employee’s gross salary be INR 10,000/ month.
- Now, the employer’s contribution will be = 3.25/100 x 10,000 = 325.
- The employee’s contribution would be = 0.75/100 x 10,000 = 75.
- Hence, the total ESI contribution in this case is INR 400.
The rates of contribution, as a percentage of gross wages payable to the employees, is explained in the table below:
| Percentage of Gross Pay | Example Gross Salary | Contributions | |
| Employee Deduction | 0.75% | INR 10,000 | 10,000 * 0.75% = 75.00 |
| Employer Contribution | 3.25% | 10,000 * 3.25% = 325.00 | |
| Total Contributions for this employee | 75.00 + 325.00 = Rs 400.00 | ||
What are the returns that are filed every year after the registration is finalized?
- Register of Attendance of the Employees.
- Form 6 – Register.
- Register of wages.
- Register of any accidents which have happened on the premises of the business.
- Monthly returns and challans.
How to file the Monthly Contribution and Payment of dues for ESI?
There are two ways to file the contribution:
- Excel Upload
- Online Entry of contribution
Excel Upload:

- Enter the 10 digit IP number, IP name, No. of Days, Total Monthly Wages, Reason for 0 wages(If Wages ‘0’) & Last Working Day (employee has left service, Retired, Out of coverage, Expired, Non-Implemented area or Retrenchment. For other reasons, the last working day must be left BLANK).
- Number of days should be the whole number. Fractions should be rounded up to the next higher Integer.
- Excel sheet upload will lead to successful transaction only when all the Employees’ (who are currently mapped in the system) details are entered perfectly in the excel sheet.
- Calculations – IP Contribution and Employer contribution calculation will be automatically done by the system.
- Reasons are assigned numeric code and date has to be provided as mentioned.
- Once 0 wages given, IP will be removed from the employer’s record. Subsequent Months will not have this IP listed under the employer.
- Note that all the columns including the date column should be in ‘Text’ format.
- Date column format is dd/mm/yyyy or dd-mm-yyyy. Pad single digit dates with 0. Eg:- 2/5/2020 or 2-May-2010 is NOT acceptable. Correct format is 02/05/2020 or 02-05-2020.

- Excel should be saved in .xls file type.
- Click on upload Excel.

Online Entry of contribution
- Click on the Submit button to also get the IPs list on the next page.

- Enter the No. of days, Total monthly wages & then click the next button for filing details on the next page. Employee Contribution will be calculated and displayed. This is rounded to the next higher rupee.
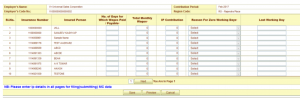
- Click the Save button, so that the Employer can also make changes later on or provide details of remaining IPs contribution.
- After entering all the contribution data in all the pages, submit the details by clicking the ‘Preview’ button, you will get a Contribution Submission Summary Page.

- Before clicking the submit button , please verify the data field , Contribution will be Submitted and you will get a Create Challan Link. (Please note-Once Contribution is submitted it can’t be modified. Employers can modify details only by filing supplementary contributions (to be explained later).
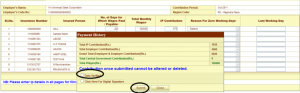
- Click on Create Challan Link, if you also want to create a challan or you can create the challan from the revenue menu.

Image source: https://www.esic.nic.in/
What is the deadline for ESI?
The contribution made by the employee towards ESI should also be deposited within the due date. It is not possible to deposit the contribution online after 42 days from the end date of the contribution period.
-
ESI payment and return filing due date
An employer should pay their contribution and the employees’ contribution on a monthly basis to the ESIC. The due date for paying ESI contributions is 15th of the following month.
Further, an employer needs to file ESI return on a half-yearly basis. Here are the due dates for filing half-yearly ESI returns:
|
Period of return |
Due date of filing returns |
| April to September | 11th November |
| October to March | 11th May |
However, these due dates can be extended or changed through an official notification by the ESIC department.
For instance, due dates of ESI contributions for the month of February 2020 & March 2020 were extended to the 15th of May 2020. Also, the due date to file ESI return for Oct’19 to Mar’20 was extended to 11th of June 2020 from 11th of May 2020.
-
Penalty for non-payment or late payment of contributions
Simple interest of 12% per annum for each day of delay in payment will also apply to every employer who fails to pay the ESI contributions on time.
Also, non-payments, delayed or false payments under the ESI Act may attract imprisonment for a period extending up to 2 years and fine up to INR 5,000.
Further, the income tax act also disallows ESI contributions deposited after the due date. The employers shall also not get the deduction benefit of such contributions and will end up paying income on it.
You may sign up for free at Asanify Payroll to automate ESI calculation, filing and payments. You may save countless hours and possible fines automating the above.
Which are the benefits under ESI?
What are the benefits for Employers under ESI?
- Employers covered under ESI Scheme are exempt from the Maternity Benefit Act and Employees’ Compensation Act for employees.
- Employers are freed from responsibility during physical distress of workers such as sickness, employment injury or physical disablement resulting in loss of wages, as the financial support in such contingencies is provided by the ESIC in respect of insured employees.
- Any sum contributed under the ESI Act is deductible while computing ‘Income’ under the Income Tax Act.
Features And Benefits of Employees State Insurance Scheme (ESIS)
1. Medical:
Under the scheme, the insured’s medical expenses are covered through affordable and reasonable health care facilities. Also, the worker or the employee is covered from day one of the person’s employment.
2. Maternity:
Under the scheme, the beneficiary can avail 100% of the daily wages for up to 26 weeks which can be extended to a further one month based on the medical advice. In the case of miscarriage, the benefit is 6 weeks, while in the case of adoption it is 12 weeks.
3. Disability:
In case of temporary disablement of the worker, they are eligible for a monthly wage of 90% until they recover. In the case of permanent disability, 90% of the monthly wage can also be availed for the entire life.
4. Sickness:
During medical leave, the scheme offers cash flow during the said period. The worker can also avail 70% of the daily wage for a maximum of 91 days. This can also be availed in two consecutive periods.
5. Unemployment:
For a period of 24 months, the scheme offers a maximum of 50% of the average monthly wage in the case of involuntary loss of non-employment or due to permanent invalidity due to injury.
6. Dependents:
Through the scheme, dependents of the insured receive financial assistance in case of illnesses or injuries while at work. During such instances, dependents are eligible for monthly payments which are equally distributed among surviving dependents.
7. Coverage:
Under the scheme, workers or employees are also covered from day one of their employment. This includes both the insured and their dependents
8. Funeral Costs:
The ESIC also offers an amount of Rs.15,000 towards funeral costs. This is paid to the dependents or to the individual who does the last rites of the insured.
9. Confinement Costs:
In case of confinement occurs at a location where required medical care under the scheme is not available, the insured or the dependent can avail confinement costs.
10. Vocational Rehabilitation:
The ESIC also provides this benefit based on the requirement of the insured. This is also extended to those who are permanently disabled injured individuals for Vocational Rehabilitation (VR) training at VRS.
11. Physical Rehabilitation:
This benefit is also provided based on the need especially in the case of disability due to employment injury.
12. Old Age Medical Care:
When the insured person retires on attaining the retirement age. Or under VRS or ERS or when a person has to leave work due to permanent disability, the insured and spouse will receive Rs.120 per annum.
ESI maternity leave application form
An insured woman can use the Form-19 to claim maternity benefit towards expected confinement or miscarriage.
No work for remuneration shall be taken up during the period for which Maternity Benefit is being claimed or is to be claimed.
- Confinement-payable for a period of 12 weeks (84 days) on production of Form 21 and 23.
- Miscarriage or Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP). Payable for 26 weeks (182 days) from the date following miscarriage-on the basis of Form 20 and 23.
- Sickness arising out of Pregnancy, Confinement, Premature birth-payable for a period not exceeding one month-on the basis of Forms 8, 10 and 9.
- In the event of the death of the Insured Woman during confinement leaving behind a child. Maternity Benefit is payable to her nominee on production of Form 24 (B).
Maternity benefit rate is 100% of average daily wages.
The below form is the Form-19 to claim for Maternity Benefit and notice of work provided by the ESIC.


What to do to claim ESI Benefit?
One can also get ESIC Form-9 to make a claim. If there should be an occurrence of Sickness/Temporary Disablement/Maternity Benefit as given by the Employees’ State Insurance Corporation, Ministry of Labor and Employment, Government of India. There are two kinds of advantages that one can guarantee as a beneficiary of the ESI scheme, as referenced below:
- Health Benefits: The employee and his/her dependents can also profit clinical consideration. To benefit this they also have to visit any of the ESI empaneled hospitals.
- Cash Benefits: Employees or laborers who are recipients of the ESI plan can profit money benefits on account of sickness, disablement (temporary/lasting), maternity, joblessness, dependent, memorial service costs, and vocational or physical recovery.
How To Check Claim Status of ESI Online?
Below are the steps to check the ESI claim status online:
- Open the UMANG App or download it if you have not installed it on your smartphone.
- Enter the IP number or the ESIC Insurance Number and click on ‘Get OTP’.
- Enter the OTP and click on ‘Submit’.
- Select ‘Claim Status’ under the services menu.
- If you have raised any claims, you will be able to view the status or you use the advanced search to find the details.
How an Automated Payroll Software helps implement Rules for ESI and PF Deduction.
Manual calculation of legal compliances includes a ton of desk work and filling in of challans and structures on paper and submitting them to banks. This also makes the cycle tedious, can present errors and can regularly prompt mix-ups.
Both the ESI and PF divisions encourage online filing and payments. It is also fitting to utilize computerized finance; preparing instruments to ascertain ESI, PF and annual duty allowances. It is also advisable to use automated payroll processing tools to calculate ESI, PF and income tax deductions.
Asanify payroll management software puts an end to increased complexities of payroll processing and offers following benefits:
- Accuracy in PF, ESI and other statutory calculations
- Increased transparency in payroll processing
- Reduced number of queries from employees
- Higher compliance
- Lower load on payroll administrators
What is the infrastructural network of ESI?
- ESI Corporation has so far set up 151 hospital and 42 hospital annexes for inpatient services.
- Primary and out-patient medical services are provided through a network of about 1418/140 ESI dispensaries/ AYUSH units, and 1017 panel clinics.
- Five Occupational Disease Centers, one each at:
- Mumbai
- New Delhi
- Kolkata
- Chennai
- Indore
for early detection and treatment of occupational diseases prevalent amongst workers employed in hazardous industries.
- For payment of Cash Benefits, the Corporation also operates through a network of over
- 627/ 185 Branch Offices/ Pay Offices
- 61 Regional/ Sub-Regional and Divisional offices supervise the functioning.
What is the Role of ESI in securing social security?
What is the social security system in India?
Ancient India
In ancient India, economic groups were also living respectively as present-day societies, represent considerable authority in various parts of the economy. Dr. R.C. Majumdar also gives a rundown of around thirty such gatherings.
The old law specialists like
- Vishnu,
- Yagnavalkya,
- Brihaspati,
- and so on,
had outlined broad laws concerning wages and states of work and specialized and vocational preparing, ladies and kid work, the guideline of mechanical relations and so forth.
These contents bear declaration to the way that social structure in those days was so included. And codes so planned as to give security to individuals when all is said in done and the laborers specifically.
Kautilya has referenced various annuity plans in his work, for example, instructive benefits, public poor relief.
In the eighth century, Sankaracharya also makes extraordinary arrangements for federal retirement aide.
Especially concerning:
- sickness advantages
- benefits
- and the mature age benefits
- family annuities
- and upkeep stipend.
He clarified that when a worker was sick and couldn’t work incidentally, the expert should make no derivation from his compensation.
Current India
In current India, it is also uniquely during the current century that the old rulers attempted to investigate; the issue of government-managed retirement that excessively is predominantly confined to the assembly line laborers and so forth.
The various meetings of the worldwide work gathering, the acknowledgment of federal retirement aide as an obligation of the state of various states in Europe and America, and advances made in these nations also roused the government of India to contemplate the issues.
- Various investigation groups and councils were also designated.
- Proposals were also given and collectively concurred that the federal retirement aide measures for the laborers in India were not satisfactory.
- Anyway, it was also predominantly after the autonomy that India could take up the issue of government-managed retirement at standard. With all serious nations of the world in an arranged and composed way.
- Free India also received the considerations of the pioneers’ pt. Jawaharlal Nehru, Sardar Valla Bhai Patel, and others.
Role of ESIC To Secure Social Security Through Benefits Available Under Employees State Insurance Act, 1948
The various benefits under this clearly shows that this is also for social security legislation. Further, a social security benefit is the provident fund. It also provides for six types of benefits to which the insured persons, their dependents and certain other entitled persons.
The benefits are as follows:
- Sickness benefit
- Maternity benefit
- Disablement benefit
- Dependents benefit
- Medical benefit
- Funeral benefit
Which prospects are Covered Under Employees’ State Insurance Scheme?
Initially, the ESI Scheme (ESIS) was implemented in Kanpur and Delhi in 1952 . These were also the two major industrial centers at that time. However, with industrial revolution picking up pace, the scheme was also adopted across the country. Over the years, with increase in industrialization, the ESIS as of 31 March 2019, was implemented in more than 34 states and Union Territories.
The ESI Act now covers nearly 12 lakh factories and business establishments and benefits more than 3 crore workers or family units. The scheme currently benefits more than 13 crore beneficiaries.
Which prospects are Not Covered Under Employees’ State Insurance Scheme?
Currently, the ESIC scheme doesn’t cover workers or employees earning more than Rs.21,000 per month. Also, in the case of a disabled person, the maximum wage is Rs.25,000/ month. Also, in Maharashtra and Chandigarh, the current threshold for coverage is still 20 employees and not 10 employees in the case of other states or UTs.
What are the futures prospects of ESI?
Inspection Scheme:
- Transparent Inspection Scheme via computerized system as per risk-based criteria, instead of arbitrary inspections based on discretion, and also uploading of Inspection Reports within 72 hours by Inspectors has been introduced.
- ESI Corporation has also extended the benefits of the ESI Scheme to the workers deployed on the construction sites located in the implemented areas under ESI Scheme w.e.f. 1st August, 2015.
- There is also a Plan to cover whole of the 393 districts, where clusters of Workers are located.
Health scheme:
- Opening Health Scheme also for selected group of unorganized workers like rickshaw pullers/auto rickshaw drivers in selected urban/metropolitan areas.
- Also, Upgrading dispensaries to six bedded hospitals in phases.
- It will also provide appropriate cancer detection/treatment facilities at different levels of hospitals.
- Also, Providing appropriate cardiology treatment facilities at different levels of hospitals.
- It also provides dialysis facilities in all ESIC Model Hospitals on PPP Mode.
- Also, Providing all possible pathological facilities in hospital premises by outsourcing or by upgrading.
- Tracking each and every mother and new born child of IP family to also achieve 100% immunization as well as safe delivery.
Creating child care hospital:
- Creating at least one Mother Child care hospital with higher facilities in every State.
- To also start setting up State ESI Corporations/Societies in all States as subsidiary of ESI Corporation.
- Electronic Health Record is also available to the IP family members online. The record will also include laboratory record in digital format and there will be no need to visit the hospital for getting this information.
- The bedsheets also have to change everyday at the ESIC hospitals and for each day of the week specific color of bed sheet has been fixed based on VIBGYOR pattern.
- ESIC Hospitals have also started to operate Special OPD every day in the afternoon from 3.00 pm to 5.00 pm for senior citizens/differently abled patients.
FAQ
Here are some important aspects that a ESI scheme you should be aware of:
1. If you switch a job, make sure that you inform the new employer of your ESI Registration Number.
2. ESI Card/Pehchan Card or e-Pehchan Card is also required to avail the services at ESI hospitals and dispensaries.
3. Follow the doctor’s instructions strictly.
The current maximum gross salary eligible for ESI is INR 21,000/month (w.e.f. 1st Jan. 2017). This means all industrial workers getting a salary of up to Rs.21,000 will be eligible for health care at more than 1,500 clinics and hospitals run by the Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) directly or indirectly.
Here are the types of establishments that can avail the ESI scheme:
1. Hotels or restaurants
2. Shops.
3. Cinemas or theatres.
4. Newspaper establishment.
5. Road transport establishment.
6. Private educational institutions.
As mandated by the ESI Act, treatment has to be taken only from the ESIC hospitals or dispensaries. However, in case of emergency, if the treatment is taken from a private hospital, you can raise a claim with the ESIC subject to ESIC approval.
Not to be considered as tax, legal, financial or HR advice. Regulations change over time so please consult a lawyer, accountant or Labour Law expert for specific guidance.




![Read more about the article The ultimate guide to filing form [GSTR – 9] online easily!](http://3.219.171.151/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/blog-covers-2240-×-1500px-43-1-300x174.webp)