The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is one of the best known strategy frameworks ever created. It’s been used by thousands of enterprises since the 1980s. Additionally it can also help startups unlock growth and even raise funds.
In this blog, I’ll tell you all you need to know about the BSC and how to implement the Balanced Scorecard in a way that drives real business value to your organization. I will be covering the following:
- What is a Balanced Scorecard?
- History of BSC
- What is Key Performance Indicator (KPI)?
- What is the difference between leading and lagging indicators?
- Which are the features of a balanced score card?
- What is the need for a balanced scorecard?
- Why does a startup need a performance management system?
- How to implement the Balanced Scorecard?
- Why is Balanced Scorecard implemented?
- What are the Benefits of Implementing the Balanced Scorecard?
- What are the problems with Implementing the Balanced Scorecard?
- Conclusion
- FAQ
What is a Balanced Scorecard?
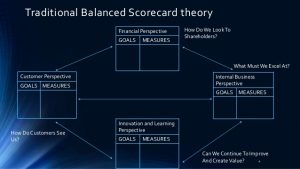
The Balanced Scorecard essentially calls for organizations to create a set of internal metrics that will help them to assess their business performance in 4 key areas, namely:
Financial
Typical scorecard metrics might include cash flow, sales performance, operating income or return on equity.
Customer
With scorecard metrics such as the following.
- % of sales from new products
- On-time delivery
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) or
- Share of wallet
Internal Business Process
This dimension helps streamline the internal processes such as the hiring policy or work from home policy. This would include measuring things such as: unit costs, cycle times, yield, error rates, etc. In a way a BSC approach helps save costs
Learning and Growth
Examples of metrics being: employee engagement scores, retention rates of high performing staff, skill increases of staff, etc. Additionally startups may want to focus on growth as a measure in itself. Measuring what matters leads to a transformation.
History of BSC
The BSC was originally developed by Dr. Robert Kaplan of Harvard University and Dr. David Norton as a framework for measuring organizational performance using a more balanced set of performance measures. Traditionally companies used only short-term financial performance as the measure of success.
The balanced scorecard added additional non-financial strategic measures to the mix in order to better focus on long-term success. The system has evolved over the years and is now considered a fully integrated strategic management system.
This new approach to strategic management was first detailed in a series of articles and books by Drs. Kaplan and Norton and built on work by Art Schneiderman at Analog Devices. Recognizing some of the weaknesses and vagueness of previous management approaches; the balanced scorecard approach provides a clear prescription as to what companies should measure; in order to ‘balance’ the financial perspective.
Kaplan and Norton describe the innovation of the balanced scorecard as follows:
The balanced scorecard retains traditional financial measures. But financial measures tell the story of past events, an adequate story for industrial age companies for which investments in long-term capabilities and customer relationships were not critical for success. These financial measures are inadequate, however, for guiding and evaluating the journey that information age companies must make to create future value through investment in customers, suppliers, employees, processes, technology, and innovation.
What is Key Performance Indicator (KPI)?
A Key Performance Indicator is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives. Organizations use KPIs at multiple levels to evaluate their success at reaching targets. High-level KPIs may focus on the overall performance of the business; while low-level KPIs may focus on processes in departments such as sales, marketing, HR, support and others.
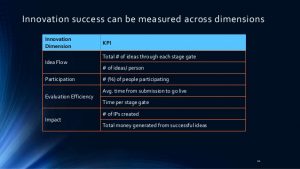
What is the difference between Leading and Lagging indicators?
Leading and lagging indicators help enterprise leaders understand business conditions and trends. They are metrics that inform managers that they are on track to meet their enterprise goals and objectives.
Leading indicator
Leading indicators are sometimes described as inputs. They define what actions are necessary to achieve your goals with measurable outcomes. They “lead” to successfully meeting overall business objectives, which is why they are called “leading”.
Lagging indicator
If a leading indicator informs business leaders of how to produce desired results; a lagging indicator measures current production and performance. While a leading indicator is dynamic but difficult to measure; a lagging indicator is easy to measure but hard to change. They are opposites, and as such a lagging indicator is sometimes compared to an output metric.
At the end, if you’re using lagging indicators without leading indicators, you’re only getting half of the KPI picture. Lagging indicators are an important resource for creating leading indicators; that can launch your business into growth mode, but they aren’t the entire package. These sets of metrics work best in pair to produce the most accurate and attainable KPIs.
Which are the features of a balanced scorecard?
The four perspectives of a balanced scorecard should be considered with respect to the following factors.
The 4 defined dimensions are give below. Note that it can be completely customized by any company.
Objectives
This reflects the organization’s objectives such as profitability or market share.
Measures
Based on the objectives, measures will also be put in place to gauge the progress of achieving objectives.
Targets
This could be department based or overall as a company. There will also be specific targets that have been set to achieve the measures.
Initiatives
These could be classified as actions that are taken to meet the objectives.

What is the need for a balanced scorecard?
You must be thinking, what’s the need for a balanced scorecard? Here are the are a few points that also describe the need for implementing a balanced scorecard:
- Increases the focus on the business strategy and also its outcomes.
- Leads to improvised organizational performance through measurements too.
- Align the workforce to also meet the organization’s strategy on a day-to-day basis.
- Targeting the key determinants or drivers of future performance.
- Improves the level of communication in relation to the organization’s strategy and also the vision.
- Helps to prioritize projects according to the timeframe and also other priority factors.
Why does a startup need a performance management system?
A BSC is also a strategy execution framework; it also helps to describe, explain, and execute strategy. It is not: a set of four perspectives to arrange KPIs. Here are the two reasons why your startup needs a BSC
Getting a Clear Understanding of the Strategy
Balanced Scorecard puts on paper the strategy of the startup. Most likely, you won’t discover any secret shortcut to become big. In reality, it is a continuous growth journey. The Balanced Scorecard framework is also about these four things:
- The expected financial results.
- Customer value proposition.
- Business processes that a company needs to have.
- Key learning and growth direction to focus on.
Pitching Idea to the Investors
BSC framework also comes from the corporate world. By having a strategy map, you send to your potential investors a simple message about the strategy and execution. A BSC provides a way to stay on track for your startup budget.
That’s similar to what non-profit organizations do when they are looking for financial donors. That’s what top managers do when they pitch their ideas internally to the board members.
How to implement the balanced scorecard?
The theory behind implementing the Balanced Scorecard is basically a series of steps.
The ability to learn and grow will directly dictate the company’s ability to better manage the internal processes. In turn, as your internal processes improve; this will have a positive impact on the customers as well as directly reducing your costs. The combined benefit of this lower cost/higher customer engagement in your product will lead to your end goal; increased profit and financial return.
The Balanced Scorecard isn’t really about distinct perspectives, it’s about the layers of a pyramid. The pyramid when built up in the right order, leads to success. When implemented in this way, the BSC can be immensely powerful in helping your organization to:
- Create a tangible road-map from the ‘current state’ to a more successful ‘future state’.
- Identify major roadblocks and areas where you lack the critical competencies to proceed to the next stage.
- Articulate how your goals will directly help the organization to move upwards through the stages.
- Prioritize business activities in the order they need to be tackled to allow the most rapid progression through the stages.
Specifically, the main benefit of the Balanced Scorecard is likely to come less from the creation of the perspectives themselves; but rather from the strategic management process using the perspectives as stages.
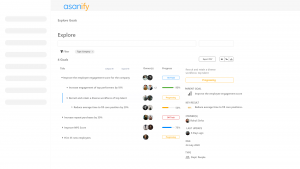
Implementing the balanced scorecard is now much easier with the Asanify Balanced Scorecard. Get started for free!
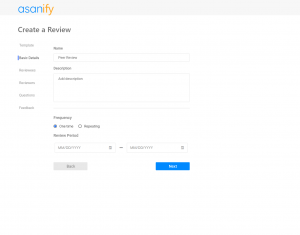
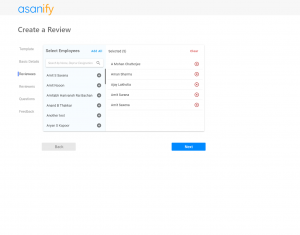
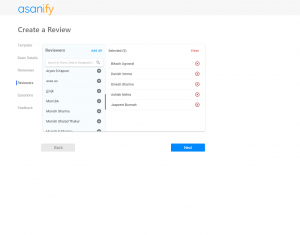
Why is Balanced Scorecard implemented?
Perspective |
Objective |
Performance measure |
Financial |
|
|
Customer |
|
|
Internal business |
|
|
Learning and Growth |
|
|
What are the Benefits of Implementing the Balanced Scorecard?
- The 4 perspectives of the BSC serve a number of purposes.
- The four perspectives also require organizations to balance their activities between the main drivers of business success.
- They also make organizations to assign tangible metrics to each perspective, increasing accountability.
- These also serve as a framework for communicating the strategy of an organization to broader stakeholders.
- Ultimately, the benefit of implementing the BSC is that it takes your organization; into a level of focus that spans both leading KPI indicators as well as lagging ones.
What are the problems with Implementing the Balanced Scorecard?
As with any popular strategic framework, the Balanced Scorecard has picked up its fair share of critics over the years. The main criticisms of the BSC are that:
- It takes too much time to set up across your company.
- People never fully understand it and therefore fail to benefit from it.
- It’s too rigid and doesn’t account for changes in the business landscape. Specifically that it’s too focused on financial measures above all else.
- It’s too internally focused, almost completely ignoring macro-economic or competitive aspects of running a business.
The truth is that the BSC is an excellent tool that when properly implemented; and will likely benefit most startups and organizations. Many of the problems with implementing the BSC come from the fact that it is so often viewed as a mere reporting framework. Using an online tool such as Asanify helps add structure to the chaos of fast growing companies.
Conclusion

- As the name denotes, a BSC creates a right balance between the components of organization’s objectives and vision.
- It’s a mechanism that helps the leadership to track down the performance of the company and can be used as a management strategy.
- It provides an extensive overview of a company’s objectives rather than limiting itself only to financial values.
- This creates a strong brand name amongst its existing and potential customers and a reputation amongst the organization’s workforce.
FAQ
The balanced scorecard (BSC) is a strategic planning and management system.
Companies use BSCs to:
Communicate what they are trying to accomplish.
Align the day-to-day work that everyone is doing with strategy. Prioritize projects, products, and services.
The balanced scorecard is made up of four perspectives; which include:
1. Financial.
2. Business process.
3. Customer.
4. Organizational capacity.
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a business framework used for tracking and managing an organization’s strategy.
The BSC framework is based on the balance between leading and lagging indicators, which can respectively be thought of as the drivers and outcomes of your company goals.
The BSC gives structure to your strategy.
The BSC makes it easy to communicate your strategy.
It aligns your departments and divisions.
The BSC helps your employees see how their individual goals link to the organizational strategy.
It keeps your strategy front and center of your reporting process.
The important difference is that KPI focuses on performance metrics, while Balanced Scorecard focuses on the business goals.
Not to be considered as tax, legal, financial or HR advice. Regulations change over time so please consult a lawyer, accountant or Labour Law expert for specific guidance.
![You are currently viewing How Balanced Scorecard [BSC] can unlock peak performance for you](https://media.asanify.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/13174345/IMG_48993.jpg)


