Maternity Leave Policy in India has been reformed considering the current scenario where women are dominantly part of any work setup. Today I will provide a template for creating a maternity leave policy for your startup or small business. Pregnancy is a phase in life; many families plan on pregnancy and childbirth. However joyous and exciting the pregnancy is, for working women the concerns prevail.
Maternity leave in India is a paid leave of absence from work that allows women employees the benefit of taking care of their newly born, and at the same time retain their jobs. The Maternity Leave Benefit Act 1961 ensured women employees get a paid leave of 26 weeks post-delivery for taking care of the new-born. Do kindly consult a professional labour law consultant for legal coverage. Today I will be covering the following:
- What is maternity leave?
- Which are the laws for maternity leave in India?
- What should a maternity leave policy include?
- What should HR incorporate in maternity leave policy?
- How to request Maternity Leave in Asanify?
- FAQ
What is maternity leave?
Maternity leave is the right for employees to take leave on giving birth. To be eligible for leave, the employee must give notice of their pregnancy in a particular form and must specify when they want their leave to start. In some situations, it can start earlier than planned (eg in some cases when the employee is sick due to a pregnancy-related reason or if they give birth prematurely).
At the earliest, this leave can be taken 11 weeks before the week in which the child is expected to be born (unless the baby is born early). Employees are required to take a minimum of 2 weeks of leave after birth.
Where does the Maternity Leave act apply?
The Maternity leave Act Applies to Establishments like:
- factories,
- corporates,
- mines,
- plantations,
- shops & establishments act,
- and government establishments.
Which are the laws for Maternity Leave in India?
The Maternity Leave in India Act 2017 Compensation rules & benefits:
- The maternity leave payment is at the rate of the average daily wage for the period of absence.
- A medical bonus is entitled in addition to the 26 weeks of paid leave & 12 weeks of paid leave for already a mother of two.
- Pregnant Women and lactating mothers further draw a benefit of Rs. 6000/- under the National Food Security Act 2013.
Norms Under The Maternity Leave:
- The act states, the employer should not give a pregnant employee difficult tasks; including long-standing working hours, ten weeks before the delivery, such that it might affect both Mother and child.
- The employer should ensure the health and safety of the female employee and mandates that she should not be involved in any work six weeks following the delivery as well as miscarriage; this also boost
- The law also states that the employer cannot dismiss or discharge a female employer during the maternity leave period.
- In an establishment of 50 plus employees, a Crèche facility is also to be provided by the employer. When the female employee comes back to work after maternity leave, she can avail of the crèche facilities. The Act also permits the female employee to visit the crèche four times during the regular working hours, including her regular rest intervals.
- If an employer does not adhere to the Maternity Act, there are severe repercussions. The penalty to an employer for non-acceptance of the Act is a fine of Rs. 5000/- or imprisonment which can extend to a year or with both.
What are the maternity benefits granted by law?
The law is fundamentally present to safeguard the interests of a mother, immediately before and after child birth. In case of infringement of those interests the law also provides the remedies for the employee adversely affected.
The law provides the following benefits:
- No woman will be asked to work in an employment for six weeks immediately preceding her delivery or miscarriage.
- Every woman will be entitled to the maternity benefits in terms of wages as prescribed in the act.
- A woman shall only be entitled to the maternity benefits under this act only if she has worked for the employer for a period of not less than one hundred and sixty days in the twelve months immediately preceding the date of her expected delivery.
- The maximum number of leaves that a woman is entitled to under the act is 26 weeks.
- A woman will not be allowed to do such work that can harm her or her child’s health during pregnancy.
- The law provides same benefits to women who have a miscarriage or tubectomy.
- A woman suffering from illness arising our of pregnancy, delivery, premature birth of child (Miscarriage, medical termination of pregnancy or tubectomy operation) be entitled, in addition to the period of absence allowed to her leave with wages at the rate of maternity benefit for a maximum period of one month.
- The law also allows employers to permit women employees to work from home in addition to the maternity benefit period if the nature of work allows that.
What should a Maternity Leave Policy include?
Eligibility
For a woman employee to be eligible under this Act; she should have completed working for 80 days in the current establishment in the last 12 months.
Salary
Paid leave is calculated based on the average daily wage for the period of absence.
Extension of period
The Maternity (Amendment) Bill 2017 has extended the earlier 12 weeks’ leave to 26 weeks. The pregnant employee can bifurcate the leave as post and pre-delivery. 8 weeks of leave can be opted before the delivery and remaining post-childbirth. For women expecting the third child, the maternity leave allotted is 12 weeks.
Maternity leave Law for adoptive mothers
The law states a 26 weeks leave for the adopting mother. This leave starts from the day of adoption and is also applicable for the baby below three months of age.
Maternity law for commissioning mothers in India
The advent of technology has also brought relief and joy to many families who were unable to conceive naturally. The maternity leave law here states a 26 week leave to the biological mother; who imparts her egg to create an embryo which is then planted in another woman.
Tubectomy during pregnancy
In the case of tubectomy, a woman on the production of the prescribed papers can also opt for two weeks’ leave; immediately from the date of the tubectomy operation.
Critical illness post-maternity
Pregnancy is a complicated process and could also be life-threatening. The Maternity leave Amendment Bill 2017 also allows a benefit of one month for women who are suffering from critical circumstances like – Pre-mature delivery, miscarriage & medical termination of pregnancy.
Leave for government civil employees
Female civil employees benefit from a paid leave of 180 days for the first two born children.
Leave for Private sector employees
Private sector female employees have to ensure maternity leave policies with their HR team. The leave and payment provisions vary for different companies.
What should HR incorporate in the Maternity Leave Policy?
- Every HR has to draft a detailed Maternity Leave Policy as an essential document. Every organization should communicate to a pregnant woman in written or e-mail about her rights and the details thereof.
- HR should revise the Maternity leave policy as per the government regulations.
- A pregnant employee is by default, exempted from the regular performance appraisal cycle.
- A provision to make the women employees work from home.
- Just like any other leave policy, maternity leave policy should also be made ready as a company document.
Alternate Policy for Maternity
There are different maternity acts under India offering maternity benefits. An organization cannot incorporate two different maternity acts at once:
ESI – Employees State Insurance: ESI is a self-financed plan and applicable for women employees, drawing a salary of 15,000/month or less. According to this Act, the employer contributes 3.25 % to the insurance, and the employee contributes 0.75 %.
The Factories Act 1948: The Factories Act ensures full wages for the 26 weeks of maternity leave.
How to request Maternity Leave in Asanify?
- You must inform the HR before starting your pregnancy leave. You should provide as much notice as possible to give your manager more time to plan for your absence. If you wish to take Sabbatical before or immediately after the maternity leave, you need to inform HR.
- You should work out an arrangement with the HR on how and when you intend to take the leave.
If the need for leave is not foreseeable, you must request the leave as far in advance as reasonably practical; (generally the same day or next day after you became aware of the need for leave). - You can submit your application for pregnancy leave on Workday along with your doctor’s certification of he expected date of delivery or relevant document for adoption before the start date of your maternity leave.
- It is your responsibility to enroll your child for medical insurance benefits within 45 days after the birth or adoption.
- You are required to enter your return to work information on Workday; no later than 7 working days prior to the scheduled end date of your leave.
- If there are any changes to the scheduled date; you must notify your manager of the new return to work date as soon as possible. Additional documentation and certification may be required. You can easily apply for maternity leave with Asanify. Get started for free!
Also Read: How to establish a leave management system
Here are the steps you need to follow while applying for a maternity leave in Asanify:
1. Apply for ‘maternity leave’ in the leave section.
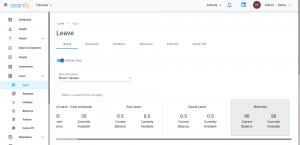
2. Select the dates you want to take leave.
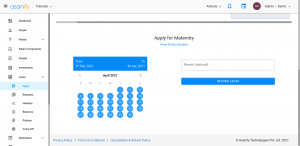
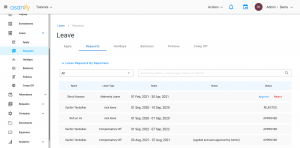
3. After you have applied for the leave, the HR can either approve or reject your leave.
FAQ
As per the Act, to be eligible for maternity leave, a woman must have been working as an employee in an establishment for a period of at least 80 days within the past 12 months. Payment during the leave period is based on the average daily wage for the period of actual absence.
For women who are having 2 or more children, the duration of paid maternity leave shall be 12 weeks (i.e. 6 weeks before and 6 weeks after expected date of delivery).
The amount of maternity pay you get changes during your maternity leave.
Depending on the legislation, maternity leave may be fully paid, partially paid or unpaid. The company will abide by legislation and it will judge whether additional benefits should be offered.
Some women begin taking their leave a week to a month before the expected birth because of discomfort or the desire for time to prepare. Others wait until the last moment so they can maximize their time with the baby once it arrives.
To create the initial part of your maternity leave plan; plan on working backwards for roughly 2 months prior.
Set a schedule of what projects and tasks you plan on accomplishing before you leave.
Not to be considered as tax, legal, financial or HR advice. Regulations change over time so please consult a lawyer, accountant or Labour Law expert for specific guidance.
![You are currently viewing [Maternity Leave Policy]: How to create one for your small business](https://media.asanify.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/24234252/christina-wocintechchat-com-YCrgxs3e9lY-unsplash-scaled.jpg)


