Every employee has the right to utilize various types of leaves in India, as required. The Indian Labor Law mandates the provision of different types of leave, of a certain quantum, to the employees of every company. These depend upon certain factors such as their period of employment, company policy, etc. Every establishment needs to give a minimum number of office leaves to its employees.
Apart from the most obvious types of paid leaves offered by companies, there are some people-centric firms that are introducing novelties in their respective leave policies for enhanced employee wellness. If you are an employer or HR professional, complying with the labor law is a must. We have prepared a list of diverse type of leaves in India that will give you a holistic idea about the various employee leaves. So, let’s dive in straight into the topic!
In today’s blog post, we will cover:
- Types of Leaves in India and Leave Policy
- Top 10 Leave Types in India
- Earned Leave or Privilege Leave- One of the Mandatory Types of Leaves in India
- Sick Leave- One of the Mandatory Types of Leaves in India
- Casual Leave- One of the Mandatory Types of Leaves in India
- Maternity Leave- One of the Mandatory Types of Leaves in India
- Paternity Leave
- Sabbatical Leave
- Bereavement Leave
- Compensatory-off or Comp-off
- Loss of Pay Leave or LOP Leave
- Time Off in Lieu or TOIL
- Other Common Types of Leaves in India- Not Mandated by Law
- Types of Leaves in India for Ventures Covered Under Various Acts
- Wrap Up
- Frequently Asked Questions- Types of Leaves in India
Types of Leaves in India and Leave Policy
In order to improve the balance between their work and personal life, employees have the right to take different office leaves during their work tenure, whether they work in a government or private organization. Studies have shown that people who are provided with a better balance between work and personal life are both- more productive and retained for a longer term.
A leave policy, therefore, emerges as a core part of HR management for every establishment. Preparing a leave policy is way too crucial for a company because it gives the employees the much-needed knowledge about the days when they can take a day off. They can also plan their vacations or other important work that they need to do urgently, on those days. After the salary figure, the second thing that employees look for, before joining, is the leave policy and the available type of leaves in that company.
You may want to check out Asanify’s Leave Management System to make adherence to the labor law mandates a breeze.
Also read- New Labor Laws: Effects on the Working Hours and Annual Leave of Employees
Why are Leave Policies Important?
One of the most important questions asked by employees when they are first recruited is about how many and what types of employees leaves they will get. Employees use their time off for various activities such as travel, spending time with friends and family, and taking part in sports and recreation.
Leave policy of a company plays a huge role in providing the employees with a basic understanding of the days when they can take time off work. Managing employee leaves and structuring the leave policy forms the mainstream of HR processes. This is because employees need to be aware if they can go for paid leave in case of sickness, accidents, emergency, or observing religious festivals, marriage ceremonies, etc.
Rules governing leave vary, depending upon the nature of business. For example, the provisions of the Factories Act of 1948 is applicable to all the factories located in India. However, if the establishment is of a different nature, and not a factory, say, companies, shops or IT firms, the provisions of the Shops and Commercial Establishments Act serve the function of guiding strictures for HR professionals to prepare the leave policy.
Let’s first understand what types of leaves in company usually exist!
Also, read – Leave policy: how to maintain compliance for your small business
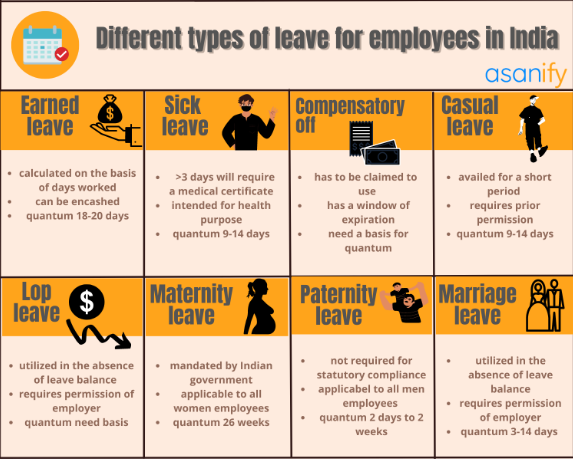
Top 10 Types of Leaves in India
Earned Leave or Privilege Leave- One of the Mandatory Leave Types in India
Employees get access to these additional leaves on a daily wage basis, and the number of days worked. The number of days for earned/privilege leave can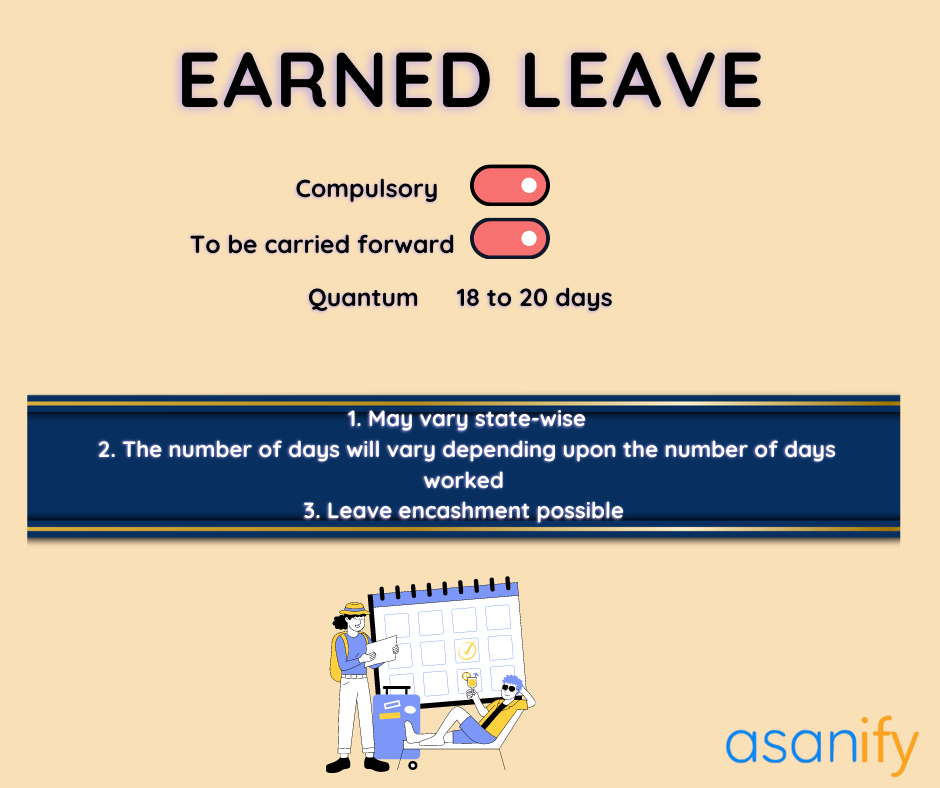 also be pushed to the next year as per the legal norms. It also entitles employees to take encashment of earned/privilege leave under the Shop and Establishment Act.
also be pushed to the next year as per the legal norms. It also entitles employees to take encashment of earned/privilege leave under the Shop and Establishment Act.
Often, privileged or earned leaves go by various names. These include:
- Vacation Leave or VL;
- Flexi Holiday;
- Annual Leave
Employees of a company utilize earned leaves to go on vacations, spend time with near ones, attend social gatherings like marriage ceremony of friends and relatives, or simply to rejuvenate their minds. As per labor law, every firm in India needs to ensure that they are offering earned leaves to its employees. However, the quantum of earned leave at each firm varies from one state to another.
The usual norm is that the employees need to inform their manager or HR that they are planning to take earned or privileged leave. Once it gets approval, they are free to spend the leave days in the way they want.
The best thing about earned leaves is that employees can encash the unused ones by the end of the year. To say in clear terms, one day of EL’s conversion through encashment results in the credit of one day’s basic pay. Depending upon the organization, gross income may replace basic pay in the calculation of leave encashment.
Sick Leave- One of the Mandatory Leave Types in India
An employee can avail sick leave in case of illness or mishaps. The State and Establishment Act has defined the number of sick leaves that employees can enjoy. These leaves also go by the name of Medical Leave or ML.
To prevent the employees from exploiting sick leaves for other not-so-genuine-reasons, employers ask for medical certificates. This is important to corroborate the entire situation. As a result, sick leave exceeding 2 or 3 days calls for the submission of a medical certificate from the employer’s end.
As per the labor law dictates, this leave type in India is compulsory. So, every company needs to ensure that they are incorporating Sick Leave or SL as a leave type in the leave policy.
The Shops and Establishments Act of various states have distinct guidelines regarding the provision of sick leave to the employees. We have discussed about the same at the end of the types of leaves in job.
Suggested Read: Types of Employment Contracts
Casual Leave- One of the Mandatory Leave Types in India
An employee may take this leave for a day or two, in case of unplanned events where he/she cannot come and work for personal reasons. This number can vary for different companies, as per the Shop and Establishment act. Casual leave cannot be clubbed with any other leave type. Also, you cannot encash or carry it forward into the next year.
Casual Leave or CL stands in contrast to Earned Leaves or EL. While the need for CL may be due to some urgent reasons like family emergency or other unforeseen circumstances that may crop up in one’s personal life, ELs come in the category of planned leaves.
The employee leave type of CL is mandatory in a majority of the states. However, some states may choose to offer integrated leave tenure by combining both the CL and SL together.
Maternity Leave- One of the Mandatory Leave Types in India
As mandated by the Maternity Benefit Act of 1961, all employers ought to grant 26 weeks of paid leave to all the female employees, who:
- are pregnant;
- have worked for a minimum of 80 days in the 12 months preceding the date of delivery
Women employees can take this leave while expecting their first two children. In case of expecting a third child, there is a provision of 12 weeks of maternity leave that female employees may utilize.
This kind of employee leave can also be taken in case of
- miscarriage;
- tubectomy;
- surrogacy
Also read- Maternity Leave Policy: How to Create One for Your Small Business?
Paternity Leave
Expectant fathers may take this leave if they need some time-off in taking care of the newborn baby and the mother. However, the certainty as to whether the employees can avail this leave depends upon the discretion of the employer. This is because it is not a mandatory leave type in India. As a result, this kind of leave doesn’t form a part of statutory compliance.
In the wake of increasing awareness about the rights of the LGBTQ community, paternity leaves also serve a crucial function for the same-sex couples. Some liberal companies have moved ahead with introducing paternity leave for their employees. In that way, all the male employees of an establishment get to dedicate a part of their lives in rearing up the baby and assisting the mother during the sensitive times.
Usually, paternity leave duration varies from 2 days to 4 weeks. There is a specific time frame within which an employee needs to apply for this leave.
If a company has incorporated paternity leave as a leave type in their leave policy, an employee needs to utilize it within 8 weeks from the baby’s birth.
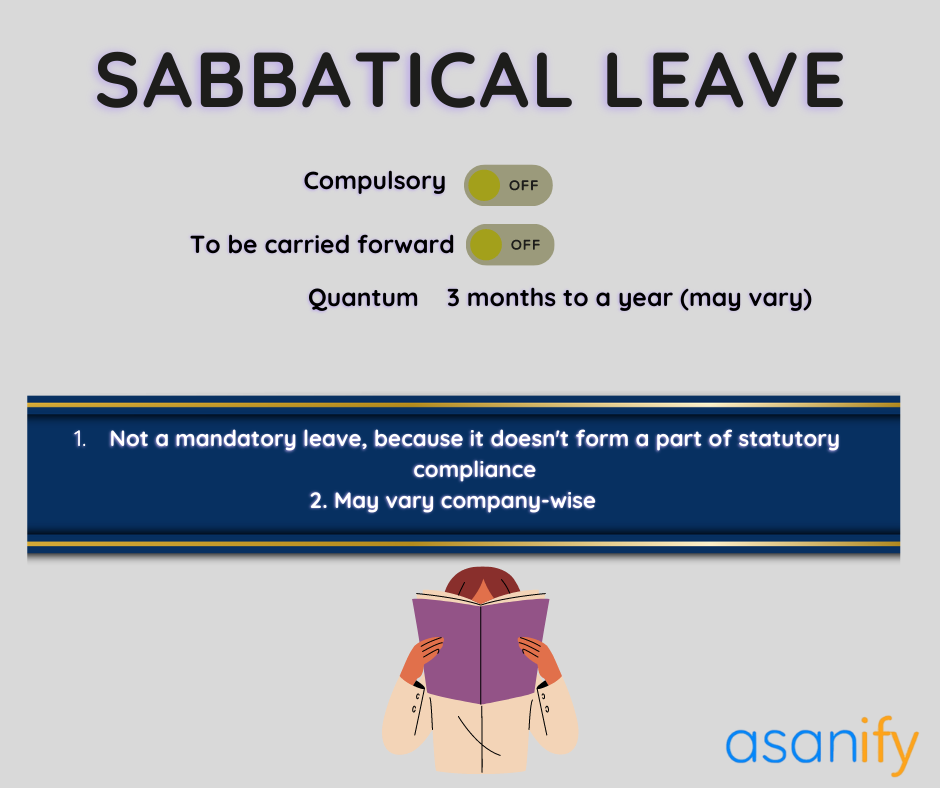
Sabbatical Leave
Sabbatical leave in India is another type of leave in India. Employees may go for sabbatical leaves if they need some time off for academic pursuits, completion of a course, or research work. It is an unpaid leave. In other words, employees won’t receive any salary while they are on sabbatical leave.
The company may require the employee to sign a bond stating that they are going to rejoin the same company after the completion of their course. In that way, an employee can contribute their newly acquired skills and knowledge to the organization.
To avail sabbatical leave, employees must have met the criteria of working in the organization for a good number of years, that is, a minimum of 2 years. However, the alteration of the rules is possible, depending upon the company. The government doesn’t mandate the provision of sabbatical leaves to company employees. Anyway, several companies are adopting this leave type in their leave policy to give their employees the scope to explore new avenues.
Apart from pursuing a course or completing any research work, employees may utilize sabbatical leave to travel overseas for gaining any skillset, or volunteering on significant projects.
Bereavement Leave
Bereavement Leave is granted to employees in case of a demise in the family. Employees can avail this leave to complete the funerary ceremonies, and cope with the tragic situation of personal loss.
The number of days under this type of leave varies company-wise. Since the labor law doesn’t mandate the provision of this leave for employees, approval of bereavement leave lies at the sole discretion of the employer. However, the usual tenure for this type of leave in India varies from 1 to 2 weeks.
Often, bereavement leave is also branded as compassionate leave. In some cases, the HR of a company may allow the employees to go for this leave so that they can take due care of a dependent family member.
Not a lot of companies in India go ahead with granting the employees this kind of leave. However, some firms with a liberal and humanistic point of view are taking bereavement or compassionate leave into consideration. In some cases, bereavement leave is offered on grounds of the death of an employee’s pet. Anyway, that has not yet emerged as a mainstream practice.
Compensatory-Off or Comp-off
If an employee works on weekends or holidays owing to mounting work pressure, they can avail compensatory-off on other work days. This is a common scenario in several companies when employees need to finish several projects or work on multiple deliverables even on holidays or after-office hours. This overtime work is rewarded in the form of compensatory-off. In that way, employees can take the much-needed break from work.
The claim for comp-off is done by submitting leave request to their managers and the HR. Once the request receives approval from the manager, it is then forwarded to the HR for further review and approval. Employees can take comp-off when the HR gives their final assent.
Since compensatory-offs come with an expiry period of 4 to 8 weeks, employees need to ensure that they are taking the leave within the specified time frame. Else, it will lapse at the year end. This kind of leave doesn’t get carried forward to the next year.
Loss of Pay Leave or LOP Leave
At times, an employee’s leave balance may get completely drained out. If they feel the need to take a day off owing to some emergency- in such a case, they may opt for Loss of Pay leave or LOP leave.
Owing to the deduction of salary, this kind of leave is known as “Loss of Pay” leave, and it is not a paid or payroll leave. At the time of payroll processing, the salary for the days, on which the employee took LOP leave, is subtracted from their net income figure.
Let’s understand this type of leave for employees with another example.
For instance, an employee doesn’t show up at work without informing their immediate manager. In such a case, that day-off would be branded as Loss of Pay Leave or LOP Leave.
To sum up, any leave that an employee takes in violation of the company leave policy or in a scenario when the existing leave balance gets exhausted, it gets counted as Loss of Pay Leave.
Time Off in Lieu or TOIL
Employees can avail this type of leave if they work overtime, surpassing the usual time frame established by the company rules. Instead of receiving extra pay, employees can avail extra leave hours that will be identical to the total number of hours they had worked overtime.
For example, if an employee works for about 46 hours instead of the established duration of 40 hours per week, they can avail extra 6 hours off. TOIL type of leave ensures the maintenance of a positive work culture in a company, and leads to enhanced employee productivity.
This is one of the leave types in office that is gradually becoming more prevalent than before. Several employees are now preferring to take extra time off instead of receiving payment for overworking. As a result, it is emerging to become quite a popular leave type in the modern workplace ecosystem.
Some companies are even coming up with a properly defined clause in their leave policy about the regulation of TOIL. It states, in clear terms, the stipulated period for which an employee can accumulate TOIL. This is important to ensure employees don’t misuse TOIL by deliberately not working in the lunch hours and later enjoying time off.
Other Common Types of Leaves in India- Not Mandated by Law
There are some leave types that the leave policy of a majority of the companies don’t make a mention of. However, there is no harm in staying acquainted with those.
Let’s see what these are!
- Military Leave;
- Jury Duty;
- Time-off for protests;
- Time-off for social work (for example, blood donation);
- Election duty
Types of Leaves in India for Ventures Covered Under Various Acts
The leaves granted to an employee by an organization will be in strict accordance with the provisions of some acts. In fact, every company drafts their respective leave policies by adhering to the mandates of the law. The structuring of the leave management in HRMS is then carried out by complying with these laws.
To ensure your organization functions in strict compliance with the labor laws, you my want to check out Asanify’s Leave Management System.
Well, so let’s first have a look at what the Factories Act of 1948 entails!
Leave Types in India Under Factories Act, 1948
The provisions stated under this act are applicable to the broad umbrella term of “workers” that includes, within its ambit:
- Workers;
- Executives;
- Supervisors;
- Contract Workers;
- Management Staff
| Items/Parameters | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per year | Leave of 1 day for every 20 days on which an employee has worked in the preceding year | —— | —— | In accordance with the mandates of the ESI Act or Maternity Benefits Act |
| Entitlement | After working 240 days in the first preceding year | —— | —— | —— |
| Usage | Leave ought to be applied 15 days in advance. Employees can’t avail leaves exceeding 3 times in a year | —— | —— | —— |
| Carry Forward | Not surpassing 30 days | —— | —— | —— |
To sum up, the salient features of this act include the following:
- Firstly, employers need to make sure that they are maintaining a proper Leave Register for all their employees.
- Secondly, to calculate leaves, Basic Wages and Dearness Allowance are important factors.
- Thirdly, in case of rejection of any worker’s leave request, the rejected leave will be carried forward to the next year.
- Fourthly, in the case of resignation or termination of an employee, the worker will receive the earned leave balance. However, in case of death, it must go to the nominee.
Types of Leaves in India Under Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, 1988
Various establishments structure their leave policy as per the Shops and Commercial Establishments Act of 1988. However, the provisions of this law vary from state to state.
Let’s have a glance at the provisions of this act, as prevailing in individual states!
Andhra Pradesh Shops and Establishments Act, 1988
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | 15 days | Not more than 12 days | Less than 12 days | Wages for 6 weeks prior to delivery and 6 weeks post-delivery |
| Entitlement | After working 240 days in a year | At the time of 12 months of service and the ensuing 12 months | During the tenure of 12 months of service and the following 12 months | Applicable to every female employee who has successfully completed either 6 months of service or more than that |
| Accumulation | For 45 days in 3 years | —— | —— | —— |
Assam Shops and Establishments Act, 1971
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity |
| Quantum per Year | For 16 days, only after an employee has worked for 12 months | 12 days for working 12 months in the establishment | For a period of 12 days, after completing 12 months of service | All the dictates of the Maternity Benefits Act of 1961 are applicable |
| Entitlement | Only after working for 240 days in a year | At the time of being employed for a constant period of 12 months | 12 months of uninterrupted employment | |
| Accumulation | Maximal limit of 30 days | —— | —— |
Bihar Shops and Establishment Act, 1953
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | Leave of 1 day can be obtained for every 20 days worked in a year | A total of 12 days | Net limit of 12 days | Will be given in the same vein, as per the provisions of Maternity Benefits Act, 1961 |
| Entitlement | For a period of 6 days; can be obtained after working for 120 days in 4 months. A minimum of 80 days form the entitlement. | At that year | During that very year | |
| Accumulation | For a maximal limit of 45 days. For instance, an employee has 45 days of leave balance in their leave management system. In case of rejection of leave request, the tenure of refused leave undergoes encashment later. | —— | —— | |
| Computation | To clarify, holidays falling within the leave period won’t be considered for computation. | |||
Asanify’s Leave Management in HRMS is what you need for absolute statutory compliance. Our delightful interface is sure to bring about enhanced employee productivity and time management.
Bombay Shops and Establishments Act, 1948
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | For a period of 21 days after having worked for 240 days in a year | —— | —— | As per the regulations established by Maternity Benefits Act, 1961 |
| Entitlement | For 5 days after 3 months. Applicable only after an employee has completed working for 60 days in that tenure. | —— | —— | |
| Accumulation | 42 days | —— | —– | |
| Computation | Holidays flanking the beginning and end points of the leave period won’t be accounted as leaves. However, holidays or Sundays falling in the middle of the leave period will fall under the computation of the leave. | |||
Delhi Shops and Establishments Act, 1954
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | Net limit of 15 days | An aggregated casual and sick leave limit of 12 days | No provisions are applicable here | |
| Entitlement | For 5 days after 3 months; only after working for about 60 days in that time period | Not less than a day for every fulfilled period of 1 month | ||
| Accumulation | 45 days in a period of 3 years | —— | —— | |
Ensuring whether your establishment has drafted the right leave policy is now just a click away. Asanify’s leave attendance management system is here to sort out things for you, while you get the chance to devote your time to other aspects of your business.
Jammu and Kashmir Shops and Establishments Act, 1966
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | Total of 15 days | For 14 days per year | —— | The mandates of the Maternity Benefit Act of 1961 are applicable. |
| Entitlement | Applicable if an employee has completed working 240 days in a year | In that very year | —— | |
| Accumulation | For 3 months to the maximum | ——– | ——- | |
| Computation | Holidays and Sundays that are falling either at the start or end point of the leave time period won’t be considered as leave. However, the company leave policy will take these as leave if these fall in the middle of the leave period. | |||
Karnataka Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, 1961
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | A leave of 1 day for every 20 days worked | —— | For 12 days | Maternity Benefit Act, 1961 is applicable here |
| Entitlement | After working 240 days in a year. However, if an employee joins in the middle of the year, they will be entitled to 2/3rd of the outstanding period in that year | —– | —— | |
| Accumulation | 30 days | —— | —— |
Click here to get your hands on a highly efficient leave management software and avert the risk of labor law compliance issues. It’s better to avert any kind of legal complexities in advance.
Kerala Shops and Establishments Act, 1948
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | For 12 days, only after serving in the establishment for 12 months | 12 day period | Usual limit of 12 days. However, additional provision of 6 days for men and 14 days for women exists, if they undergo any sterilization operation. | In strict adherence to the Maternity Benefits Act of 1961 |
| Accumulation | For 24 days in 2 years | —— | —— |
Madhya Pradesh Shops and Establishments Act, 1948
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave | |
| Quantum per Year | For 30 days only after being employed in the firm for 12 months | 14 days | – | All the regulations established by the Maternity Benefit Act of 1961 are applicable. | |
| Entitlement | 5 days after being employed for 3 months (applicable after working for 60 days in that timeline) | During that very year | – | ||
| Accumulation | Total of 90 days in 3 years | — | — | ||
| Annexation | Casual leaves can not be annexed with earned leave. Holidays and Sundays that are falling at either points of the leave time period do not fall in the category of leaves. However, these will come under the category of leave if these fall in the midst of the leave period. | ||||
Are you worried if your organization is adhering to the labor laws with precision? Click here to put that stress to rest.
Odisha Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, 1948
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | Leave of 1 day can be taken for every 20 working days | —— | 15 days | Every female employee is eligible for 6 weeks of leave preceding the delivery date and 6 weeks post-delivery, only if they have been employed for a continuous stretch of 6 months or beyond. |
| Entitlement | After working 240 days in a year. However, an employee may join in the mid-year. In that case, the entitlement will be for 2/3rd of the remaining period in that year. | —— | —— | |
| Accumulation | 30 days
(For example, an employee has 30 ELs to their credit. In case of rejection of leave, accumulation of leaves is possible.) |
—— | —— | |
| Computation | Holidays or Sundays lying at the two ends of the leave tenure won’t be considered as leave. | |||
Punjab Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, 1958 (followed by Haryana, as well)
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | Provision of leave for every 20 days worked | 7 days | 7 days | All female employees can get Maternity Leave of 6 weeks prior to the delivery date and 6 weeks post-delivery, if they were employed for 6 months at a stretch. |
| Entitlement | Post-20 days of continuous employment | During that year | During that year | |
| Accumulation | 30 days | —— | —— |
Rajasthan Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, 1958
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | Leave of 1 day for every 20 days worked | —— | —— | Every woman, who has been engaged in uninterrupted employment of 6 months, can get leave of 6 weeks prior to the delivery date and 6 weeks post-delivery. |
| Accumulation | 30 days | —— | —— |
Tamil Nadu Shops and Establishments Act, 1958
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | For a period of 12 days | Net tenure of 12 days | Maximum tenure of 12 days | All the provisions of the Maternity Benefit Act, 1961 are applicable here |
| Accumulation | 24 days | —— | —— |
Uttar Pradesh Shops and Establishments Act, 1962
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | Leave of 15 months for every 12 months of uninterrupted employment | 10 days | 15 days | All the provisions of Maternity Benefit Act of 1961 are applicable here |
| Entitlement | After completion of 1 year of constant employment | Only after 6 months of continuous employment | ||
| Accumulation | For 45 days in 3 years | —— | —— |
Leave Management System by Asanify has been designed with an aim to simplify HR processes. You can save time to build and grow your business while letting Asanify do the magic. All the mandatory HR tasks, starting from leave management to payroll generation, and much more, will be simplified with Asanify.
West Bengal Shops and Establishments Act, 1963
| Items | Earned Leave or EL | Casual Leave or CL | Sick Leave | Maternity Leave |
| Quantum per Year | Leave of 14 days for every fulfilled year | For 10 days. However, employees can’t take leave for 3 days at a continuous stretch. | For 14 days each year.
Chances of payment deduction exist. |
All female employees can take Maternity Leave for 6 weeks prior prior to the delivery date and 6 weeks after the delivery of the baby, only if they have completed 6 months of steady employment |
| Entitlement | Only after completion of 1 year of employment | In that very year | During that year itself | |
| Accumulation | 24 days in a period of 2 years | —— | —— |
Wrap Up
Well, so that’s all about the various types of leaves in India prevailing at the moment. Now that you are well-aware of the existing leave types for employees, structuring your company leave policy will be a cakewalk now. However, if you are still unsure about complying with labor laws, Asanify is here to save your time in complying with these very laws while also taking care of various other aspects of people management in your firm. So, just de-stress and let Asanify rob all your worries away!
Frequently Asked Questions- Types of Leaves in India
1. What are the different types of employee leave?
The various types of employee leave include voluntary, involuntary, paid and non-paid leave.
2. What is the difference between EL and CL?
While an employee’s CL or Casual Leave accounts for leave used for some personal reasons, EL refers to planned leaves. Employees can use the latter for going on vacations or any other planned event. An employee gets EL or Earned Leave only after working for a certain period of time in an establishment.
3. Is casual leave paid?
Yes, casual leave is a kind of paid leave. Usually, employees can avail it for a maximum of 3 days at a stretch.
4. What is PH in attendance?
A PH or Personal Holiday in attendance refers to a paid leave that employees can use in a calendar year.
5. What is without pay leave?
A without pay leave is the other word for Loss of Pay Leave or LOP Leave. In case of exhaustion of leave balance of an employee, they may go for LOP leave with their manager’s permission. In such a case, deduction of a day’s salary from the basic pay takes place.
6. Is medical certificate a must for 3 days sick leave?
Yes, in case of taking sick leave beyond 2 or 3 days, employees need to produce a medical certificate before their employers.
Not to be considered as tax, legal, financial or HR advice. Regulations change over time so please consult a lawyer, accountant or Labour Law expert for specific guidance.